Chapter 8 System BIOS
8.3.3 MEMORY DETECTION AND CONFIGURATION
This system uses the Serial Presence Detect (SPD) method of determining the installed DIMM
configuration. The BIOS communicates with an EEPROM on each DIMM through the SMBus to
obtain data on the following DIMM parameters:
♦
Presence
♦
Size
♦
Type
♦
Timing/CAS latency
♦
Memory speed
NOTE:
Refer to Chapter 3, “Processor/Memory Subsystem” for the SPD format and
DIMM data specific to this system.
The BIOS performs memory detection and configuration with the following steps:
1.
Program the buffer strength control registers based on SPD data and the DIMM slots that are
populated.
2.
Determine the common CAS latency that can be supported by the DIMMs.
3.
Determine the memory size for each DIMM and program the graphics controller accordingly.
4.
Enable refresh
5.
Determine if the memory configuration will allow for double-clocked 133-MHz memory
operation and program the memory clock and IGP (see note below)
NOTE:
The BIOS must read a value of 07h (indicating DDR) from SPD byte 02h of
each DIMM in order to validate the memory.
8.3.4 BOOT ERROR CODES
The BIOS provides visual and audible indications of a failed system boot by using the keyboard
LEDs and the system speaker. The error conditions are listed in the following table.
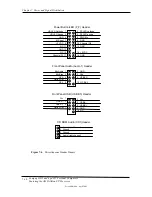
Table 8-2. Boot Error Codes
Table 8-2.
Boot Error Codes
Visual [1]
Audible
Meaning
Num Lock LED blinks
1 short, 2 long beeps
System memory not present or incompatible.
Scroll Lock LED blinks
2 long, 1 short beeps
Hardware failure before graphics initialization.
Caps Lock LED blinks
1 long, 2 short beeps
Graphics controller not present or failed to
initialize.
Num, Caps, Scroll Lock LEDs
blink
1 long, 3 short beeps
ROM failure.
Num, Caps, Scroll Lock LEDs
blink in sequence
none
Network service mode
NOTE:
[1] Provided with PS/2 keyboard only.
Compaq D315 and hp d325 Personal Computers
Featuring the AMD Athlon XP Processor
Second Edition - April 2003
8-4