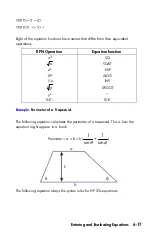
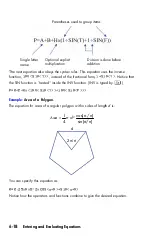
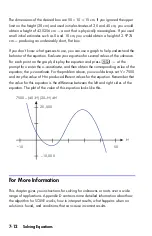
7-4
Example:
Solving the Ideal Gas Law Equation.
The Ideal Gas Law describes the relationship between pressure, volume,
temperature, and the amount (moles) of an ideal gas:
P
×
V
=
N
×
R
×
T
where
P
is pressure (in atmospheres or N/m
2
),
V
is volume (in liters),
N
is the
number of moles of gas,
R
is the universal gas constant (0.0821 liter–atm/mole–K
or 8.314 J/mole–K), and T is temperature (Kelvins: K=°C + 273.1).
Enter the equation:
Keys:
Display:
Description:
Displays the equation.
Solves for
T
; prompts for
D
.
Stores 500 in
D
; prompts
for
V
.
Retains 0 in
V
; prompts
for
G
.
Retains 9.8 in
G
; solves
for
T
.
Keys:
Display:
Description:
P
_
Selects Equation mode
and starts the equation.
_
Terminates and displays
the equation.
Checksum and length.
Содержание 35s
Страница 1: ...HP 35s scientific calculator user s guide H Edition 1 HP part number F2215AA 90001 ...
Страница 14: ...12 Contents ...
Страница 15: ...Part 1 Basic Operation ...
Страница 16: ......
Страница 46: ...1 30 Getting Started ...
Страница 63: ...RPN The Automatic Memory Stack 2 17 A Solution ...
Страница 64: ...2 18 RPN The Automatic Memory Stack ...
Страница 74: ...3 10 Storing Data into Variables ...
Страница 180: ...12 14 Statistical Operations ...
Страница 181: ...Part 2 Programming ...
Страница 182: ......
Страница 246: ...15 12 Solving and Integrating Programs ...
Страница 270: ...16 24 Statistics Programs ...
Страница 284: ...17 14 Miscellaneous Programs and Equations ...
Страница 285: ...Part 3 Appendixes and Reference ...
Страница 286: ......
Страница 308: ...B 8 User Memory and the Stack ...
Страница 322: ...C 14 ALG Summary ...
Страница 336: ...D 14 More about Solving ...
Страница 346: ...E 10 More about Integration ...
Страница 352: ...F 6 Messages ...
Страница 370: ...G 18 Operation Index ...
Страница 382: ...Index 12 ...