52
1019658 11/2014
Collision torque T
M
[Nm]
In the event of an emergency stop or collision, the Harmonic Drive® Gearing may be subjected to a brief collision torque.
The magnitude and frequency of this collision torque should be kept tom a minimum and under no circumstances should
the collision torque occur during the normal operating cycle.
Continuous stall current I
0
[A
rms
]
Effective value of the motor phase current to produce the stall torque.
Continuous stall torque T
0
[Nm]
Allowable actuator stall torque.
Demagnetisation current I
E
[A
rms
]
Current at which rotor magnets start to demagnetise.
Dynamic axial load F
A dyn (max)
[N]
With bearing rotating this is the maximum allowable axial load, with no additional radial forces or tilting moments applied.
Dynamic load rating C [N]
Maximum dynamic load that can be absorbed by the output bearing before permanent damage may occur.
Dynamic radial load F
R dyn (max)
[N]
With bearing rotating this is the maximum allowable radial load, with no additional axial forces or tilting moments applied.
Dynamic tilting moment M
dyn (max)
[Nm]
With the bearing rotating this is the maximum allowable tilting moment, with no additional axial forces or radial forces
applied.
Electrical time constant
τ
e
[s]
The electrical time constant is the time required for the current to reach 63% of its final value.
Hollow shaft diameter d
H
[mm]
Free inner diameter of the continuous axial hollow shaft.
Inductance (L-L) L
L-L
[mH]
Terminal inductance calculated without taking into account the magnetic saturation of the active motor parts.
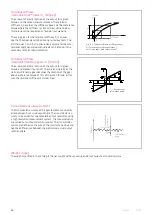
Lost Motion (Harmonic Drive® Gearing) [arcmin]
Harmonic Drive® Gearing exhibits zero backlash in the teeth.
Lost motion is the term used to characterise the torsional
stiffness in the low torque region.
The illustration shows the angle of rotation
ϕ
measured
against the applied output torque as a hysteresis curve, with
the Wave Generator locked. The lost motion measurement of
the gear is taken with an output torque of about ± 4% of the
rated torque.
Torsion
φ
Torque T
~ +4%T
N
~ -4%T
N
Lost M
otion
φ
1
;
φ
2
φ
1‘
;
φ
2‘