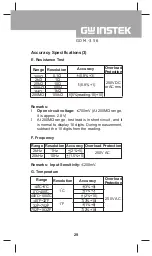
23
Measurement Operation(11)
Note
l
For testing the capacitor with polarity, connect the
red test lead to anode & black test lead to cathode
l
When the tested capacitor is shorted or the capacitor
value is overloaded, the LCD display
“1”
.
l
To minimize the measurement error caused by the
distributed capacitor, the testing lead or testing clip
should be as short as possible.
When the tested capacitor is greater than 30
µ
F,
reading is for reference only.
l
It is normal to take a while for zeroing when changing
over the measurement range. This process will not
affect the accuracy of the final readings obtained.
I. Measuring Diodes & Continuity
Warning
To avoid damage to the Meter or to the equipment
under test, disconnect circuit power and discharge
all high-voltage capacitors before measuring diodes
and continuity.
Testing Diodes
Use the diode test to check diodes, transistors, and other
semiconductor devices. The diode test sends a current
through the semiconductor junction, and then measures
the voltage drop across the junction. A good silicon
junction drops between 0.5V and 0.8V.
To test out a diode out of a circuit, connect the Meter as
follows:
1. Insert the red test lead into the
V
Ω
terminal and
the black test lead into the
COM
terminal.
2. Set the rotary switch to
.
3. For forward voltage drop readings on any semiconductor
component, place the red test lead on the component’s
anode and place the black test lead on the component’s
cathode.
The measured value shows on the display.
GDM-356