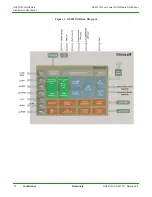
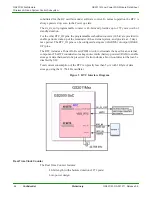
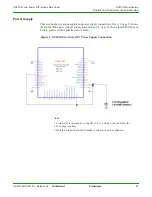
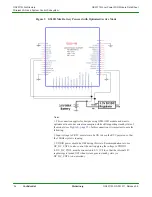
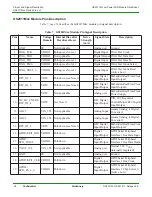
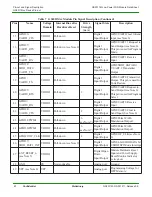
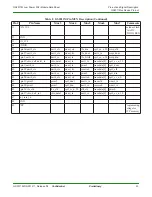
GS2011M Architecture
GS2011M Low Power WiFi Module Data Sheet
Wireless LAN and System Control Subsystem
28
Confidential
Preliminary
GS2011M-DS-001211, Release 0.9
•
Allows card to interrupt host in SPI, 1 and 4 bit SD modes
•
Read and Writes using 4 parallel data lines
•
Cyclic Redundancy Check CRC7 for command and CRC16 for data
integrity-CRC checking optional in SPI mode
•
Programmable through a standard AHB Slave interface
•
Writing of the I/O reset bit in CCCR register generates an active low reset output
synchronized to AHB Clock domain
•
Card responds to Direct read/write (IO52) and Extended read/write (IO53)
transactions
•
Supports Read wait Control operation
•
Supports Suspend/Resume operation
SPI Interface
The SPI interface is a master slave interface that enables synchronous serial
communications with slave or master peripherals having one of the following: Motorola
SPI-compatible interface, TI synchronous serial interface or National Semiconductor
Microwire interface. In both master and slave configuration, the block performs
parallel-to-serial conversion on data written to an internal 16-bit wide, 8-deep transmit
FIFO and serial to parallel conversion on received data, buffering it in a similar 16-wide, 8
deep FIFO. It can generate interrupts to the CPU to request servicing transmit and receive
FIFOs and indicate FIFO status and overrun/underrun. The clock bit rate is SW
programmable. In master mode, the SPI block in GS2000 can perform up to 30 MHz and
in slave mode up to 10 MHz serial clock. The interface type, data size and interrupt masks
are programmable. It supports DMA working in conjunction with the uDMA engine.
UART Interface
The UART interface implements the standard UART protocol. It is 16450/16550
compatible. It has separate 32 deep transmit and receive FIFOs to reduce CPU interrupts.
The interface supports standard asynchronous communication protocol using start, stop and
parity bits. These are added and removed automatically by the interface logic. The data size,
parity and number of stop bits are programmable. It supports HW based flow control
through CTS/RTS signaling. A fractional baud rate generator allows accurate setting of the
communication baud rate. It supports DMA working in conjunction with the uDMA
engine.
I2C Interface
The I2C interface block implements the standard based two wire serial I2C protocol. The
interface can support both master and slave modes. It supports multiple masters, high speed
transfer (up to 3.4MHz), 7 or 10 bit slave addressing scheme, random and current address
transfer. It also supports clock stretching to interface with slower devices. It can generate
interrupts to the CPU to indicate specific events such as FIFO full/empty, block complete,
no ack error, and arbitration failure.