5
Folks sometimes ask us, "why isn't there extra mixer circuitry included
with the Wave/4"? When we designed the Wave/4 card, we concluded
that having a built-in mixer would make it more complicated to use the
card in conjunction with an external mixer. Also, when extra mixer
circuitry is included in a sound card, an extra level of amplification is
required. This might diminish audio quality and add noise. So the
Wave/4 design follows the same model set by the popular CardD+ PC
audio card (a very high quality card). We decided to avoid needless
complexity and preserve the highest audio quality.
Connecting the Wave/4 to a mixer
Below are some block diagrams for connecting the Wave/4 card to a
mixer. The Wave/4 card can be used with a wide variety of mixers that
are available from many different manufacturers. If you are consider-
ing the purchase of a mixer for your recording setup, you can buy a
small line-level mixer; we've seen them as low as US $150. A more
flexible option would be a small console with prices that start at
around US $300.
If your mixer has channel inserts (also called patch points), for quietest
operation, we recommend that you directly patch the Wave/4 inputs to
the channels at the inserts points. This offers maximum mixing
flexibility and allow you to monitor all the Wave/4 inputs and outputs
as you're recording.
Connections for Wave/4 to mixer with channel inserts
Mixer Input Channels
Ch1 Ch2
L R L R
Wave/4 card
OUTPUT
Microphones
Guitar rig
Keyboards, etc.
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8 ...
Channel Inserts
...
L R L R
Ch1 Ch2
Wave/4 card
INPUT
Mixer outputs
Connect to monitor
amp, DAT, etc.
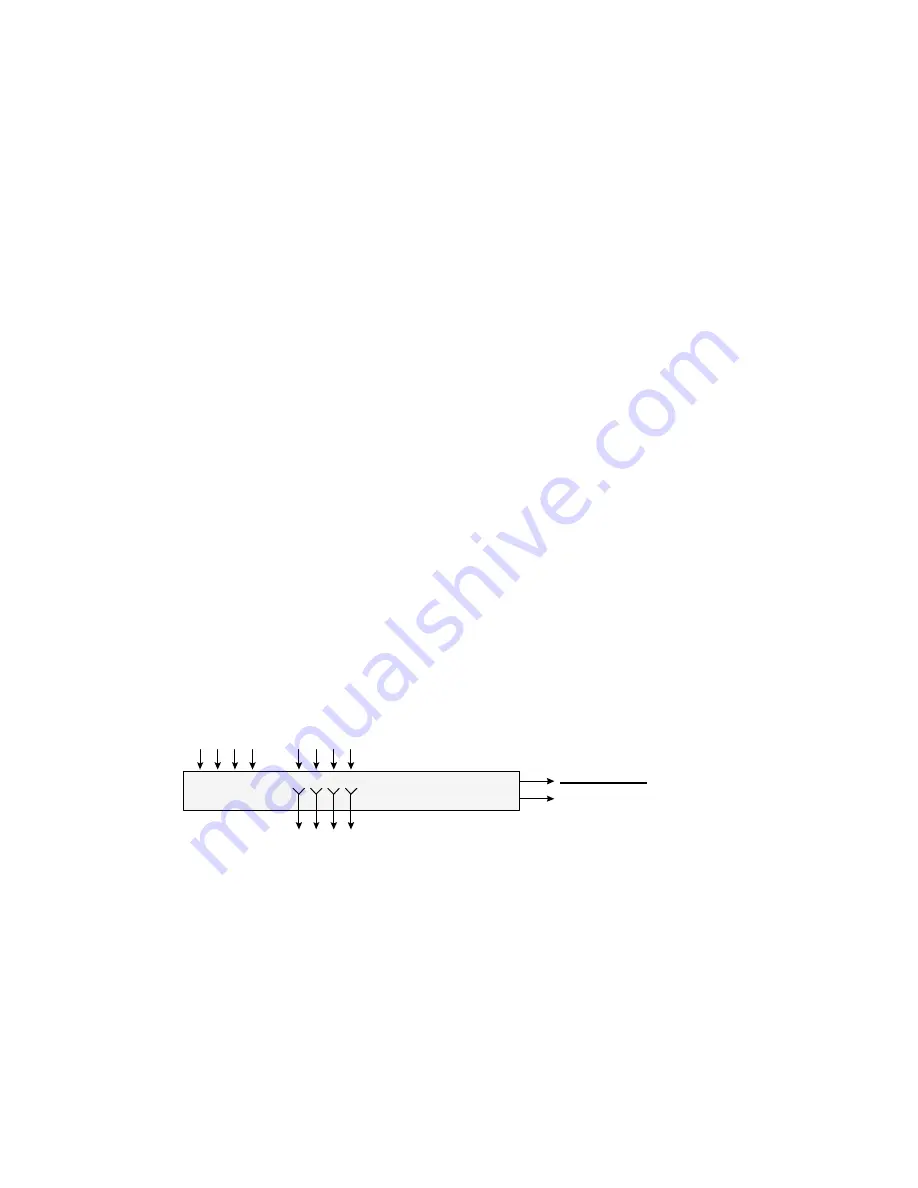
If your mixer does not have channel inserts, you can achieve similar
flexibility by splitting the input signal prior to the mixer with Y-
adapters. Since the Wave/4 requires a line level signal, you will need
to make sure that any low-level signals, such as microphones, are
preamplified prior to the signal split.






































