30
3
Memory Configuration
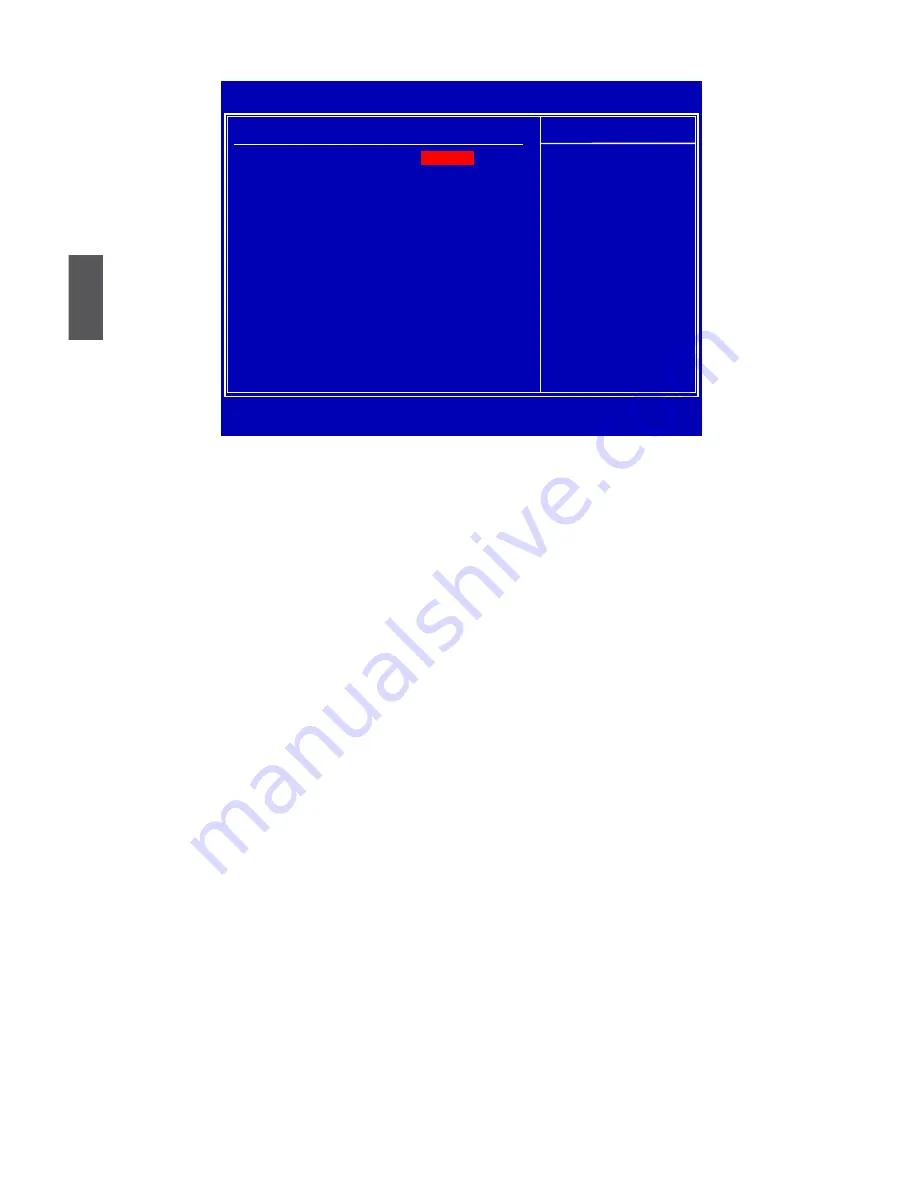
CMOS Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 1985-2008, American Megatrends, Inc.
Memory Configuration
Memory Configuration
Help Item
Bank Interleaving
[Disabled]
Enable bank Memory
Channel Interleaving
[Enabled]
I interleaving
DCT Unganged Mode
[Always]
↑↓←→:Move Enter:Select +/-/:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F1:General Help F9:Optimized Defaults
[Disabled]
► Bank Interleaving
Interleaving allows banks of SDRAM to alternate their refresh and access cycles. One
bank will undergo its refresh cycle while another is being accessed. This improves memory
performance by masking the refresh cycles of each memory bank. However, bank interleaving
only works if the addresses requested consecutively are not in the same bank.
► Channel Interleaving
Dual channel (Interleaved) mode offers the highest throughput for real world applications. Dual
channel mode is enabled when the installed memory capacities of both DIMM channels are
equal. If different speed DIMMs are used between channels, the slowest memory timing will be
used.
► DCT Unganged Mode
DCT stands for DRAM Controller.
Ganged refers to the use of both DRAM controllers within a memory controller acting in con-
cert to access memory. For a description of ganged (128-bit DRAM data width) and unganged
(64-bit DRAM data width) DRAM modes :
Ganged channels (DDR2) :
■
DCT channels A and B can be ganged as a single logical 128-bit DIMM.
■
Offers highest DDR2 bandwidth.
■
Requires both DIMMs in a logical pair to have identical size and timing parameters, both
DCTs programmed identically.
Unganged channels
■ DCT channels A and B operate as two completely independent 64-bit channels (both chan
-
nels operate at the same frequency).
■ Reduce DRAM page conflicts – more concurrent open dram pages .
■ Better bus efficiency.
Burst lengths supported
When both DCTs are enabled in unganged mode, BIOS must initialize the frequency of each
DCT in order.