PG9602™ OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
© 2011 Fluke Calibration
Page
56
•
differential (dif)
: Defines differential pressures at an absolute static pressure between
vacuum and two atmospheres by defining an absolute pressure relative to an evacuated
bell jar and subtracting static pressure monitored by a digital pressure indicator. An
offsetting technique ensures that only the digital indicator’s resolution and very short term
repeatability influence the measurement results. Allows positive and negative differential
pressure (including gauge pressures) with one common hardware setup. Covers
pressures very near and at zero without limitations due to piston-cylinder size and mass
loads (see Section 3.10.4.1).
OPERATION
To change the pressure measurement mode, press
[MODE]
from any run screen. The resulting
display depends on the PG9000 Model:
The cursor is on the number corresponding to the current measurement mode.
Measurement mode:
1g 2avac 3aatm 4dif
Selecting
<2avac>
enables
absolute by vacuum
mode. Selecting
<3aatm>
enables
absolute
by ATM
mode. Selecting
<4dif>
enables
differential
mode.
Making a measurement mode selection returns to the previous run screen with the selected
mode active.
Note
When using an AMH, be sure to apply drive vacuum to the AMH when
switching operation to absolute by vacuum mode (see 3.7.2.5).
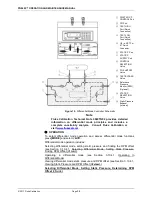
3.10.4.1 Differential Measurement Mode
PURPOSE
To define gauge pressures near and under atmospheric pressure that cannot be
covered in conventional gauge mode; to define pressures at a static pressure
near atmospheric pressure but other than atmospheric pressure.
Note
Differential mode operation requires additional hardware and
that the PG9000 SETUP selection for AtmP be configured for an
external barometer connected to COM2 (see Section 3.11,
3.12.5.4). Differential mode operation also requires the PG9000
Differential Mode Interconnections kit P/N 3070127, which
includes the Differential Mode housing.
PRINCIPLE
Differential mode is designed to allow PG9000 to define pressures which piston
gauges have typically not covered or for which they have been difficult to use.
This includes positive and negative gauge pressures near zero, for example
± 2.5 kPa (10 in. H2O); as well as low differential pressures at low absolute static
pressures, for example 0 to 2.5 kPa (20 Torr) at 15 kPa absolute (2.2 psia) static
pressure.
The principal of differential mode is to define a differential pressure as the
difference between an absolute pressure relative to vacuum and a second
absolute pressure (the static pressure) measured by a precision Reference
Pressure Monitor (RPM). An offsetting procedure “tares” the RPM so that the
uncertainty contributed to the differential pressure by the RPM’s measurement is
a function of the RPM resolution and short term repeatability rather than its
absolute accuracy and long term stability.
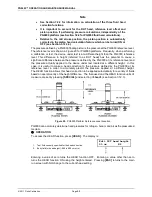
For differential mode operation, the static pressure is set to the desired value as
measured by the RPM (atmospheric pressure for gauge pressure
measurements). The RPM offset at the static pressure is determined by applying
the static pressure as defined by the PG9000 following:
Содержание PG9000 Series
Страница 10: ...PG9602 OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL 2011 Fluke Calibration Page X Notes...
Страница 128: ...PG9602 OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL 2011 Fluke Calibration Page 118 Notes...
Страница 164: ...PG9602 OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL 2011 Fluke Calibration Page 154 Notes...
Страница 188: ...PG9602 OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL 2011 Fluke Calibration Page 178 Notes...
Страница 192: ...PG9602 OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL 2011 Fluke Calibration Page 182 Notes...