6.4
Device information (participant characteristics)
In the initialisation of the bus node, the I-Port device information is written to the
following memory areas:
I/O addresses
1)
Start address
(Offset)
Data field
size
I-Port 1
Input data length
16#0200
1 Byte
Output data length
16#0201
1 Byte
IO-Link Vendor ID
2)
16#0202
2 Bytes
IO-Link Device ID
2)
16#0204
4 Bytes
Product Name [String]
16#0208
65 Bytes
Order Code [String]
16#0249
65 Bytes
Product Text [String]
16#028A
65 Bytes
Serial Number [String]
16#02CB
17 Bytes
Hardware Revision [String]
16#02DC
65 Bytes
Firmware Revision [String]
16#031D
65 Bytes
I-Port 2
Input data length
16#0400
1 Byte
Output data length
16#0401
1 Byte
IO-Link Vendor ID
2)
16#0402
2 Bytes
IO-Link Device ID
2)
16#0404
4 Bytes
Product Name [String]
16#0408
65 Bytes
Order Code [String]
16#0449
65 Bytes
Product Text [String]
16#048A
65 Bytes
Serial Number [String]
16#04CB
17 Bytes
Hardware Revision [String]
16#04DC
65 Bytes
Firmware Revision [String]
16#051D
65 Bytes
1) The specified start addresses refer to the basic address stipulated by the PLC.
2) "IO-Link Vendor ID" and "IO-Link Device ID" ae dependent on the connected product.
Tab. 7
"Vendor ID" and "Device ID" of the bus node CTEU-VN in the VARAN-BUS net-
work:
•
Vendor ID: 15
•
Device ID: 1281
7
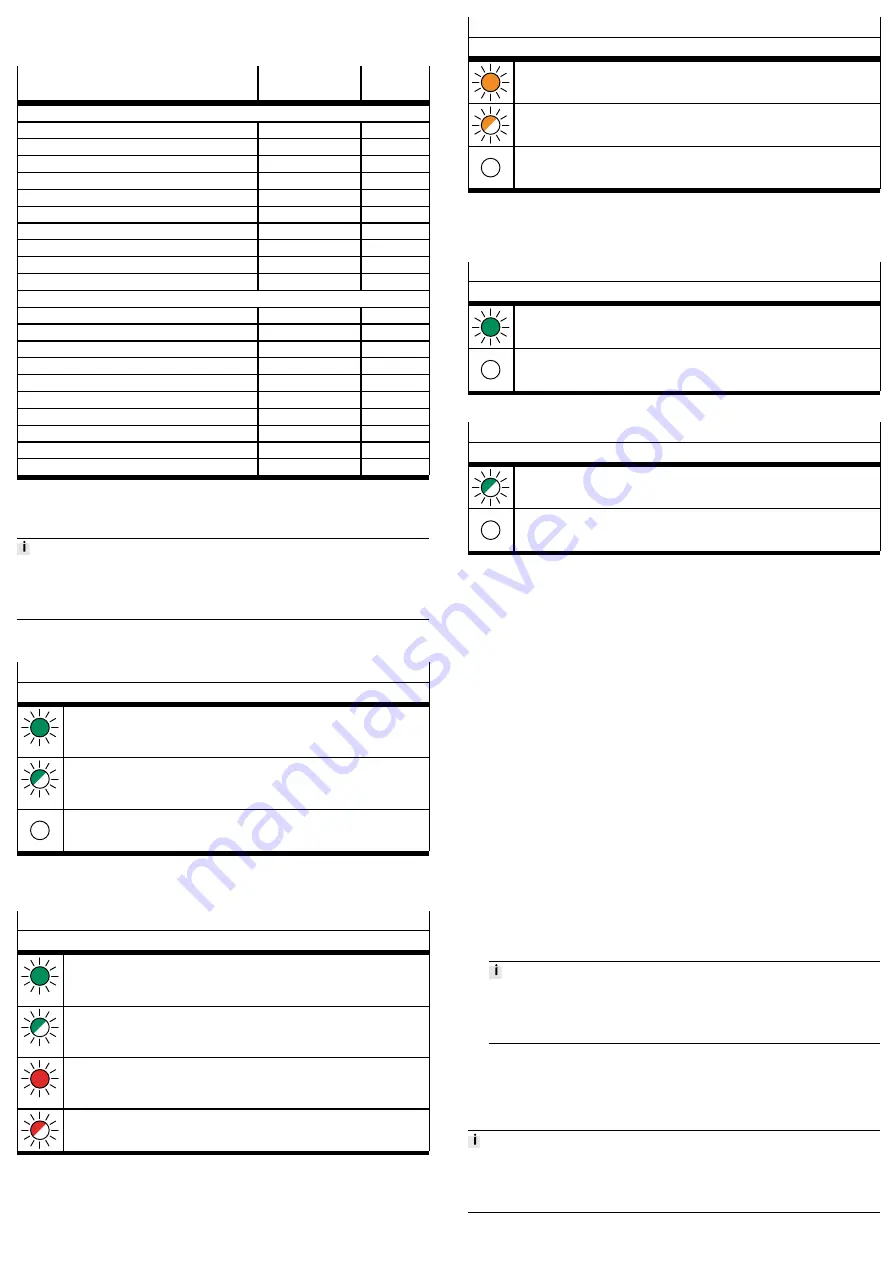
Diagnostics via LEDs
PS
–
Status of the operating and load voltage supplies
LED status and meaning
LED lights up green:
–
Normal operating status
–
Operating voltage is present (within the permissible range)
–
Load voltage is present (within the permissible range)
1)
LED flashes green (flashing frequency: 1 Hz):
–
Operating voltage is below the required voltage
–
Load voltage is below the required level
1)
–
Short circuit at the I-Port
1)
LED is off:
–
Operating voltage is not present
–
Operating voltage is below the minimum voltage required for diagnostic functions
1) This display only relates to the status of the load voltage if the connected product is monitoring the load
voltage and reports its status to the bus node.
Tab. 8
X1 and X2
–
System status "I-Port Device 1" or "I-Port Device 2"
1)
LED status and meaning
LED lights up green:
–
Normal operating status
–
I-Port device 1 or 2 is connected correctly
–
Operating and load voltages are present (within the permitted range)
2)
LED flashes green:
–
Status of diagnostics
–
Undervoltage at system or additional supply
–
Connection between the bus node and the I-Port device is OK
LED lights up red:
–
I-Port device is connected correctly, but the internal communication is malfunction-
ing
–
After commissioning, I-Port Device removed
LED flashes red:
–
Error in the bus node
X1 and X2
–
System status "I-Port Device 1" or "I-Port Device 2"
1)
LED status and meaning
Both LEDs light up orange:
–
Firmware update active
Both LEDs flash orange:
–
To locate the bus node (“module location”), e.g. during hardware configuration in
the control system or for troubleshooting
LED is off:
–
No product connected to the bus node
1) Accessories with two I-Port interfaces required for connecting two products
2) This display only relates to the status of the load voltage if the connected product is monitoring the load
voltage and reports its status to the bus node.
Tab. 9
XF1 LI
–
Connection status IN XF1 ("Link")
LED status and meaning
LED lights up green:
–
Normal operating status
–
Network connection is OK
LED is off:
–
No network connected
Tab. 10
XF1 AC
–
Data reception IN XF1 ("Active")
LED status and meaning
LED flashes green:
–
Data traffic
LED is off:
–
No data reception
Tab. 11
8
Firmware update
A firmware update can only be performed by the Festo Field Device Tool (FFT)
è
8.1
Preparation of Firmware update
For the Firmware update, the bus node must be connected with the Ethernet con-
nection of a PC or with the LAN via the network connection IN XF1.
The bus node independently detects the Ethernet connection and changes the
connection protocol correspondingly from VARAN-BUS to Ethernet communica-
tion. The Ethernet connection is addressed as part of the preparation via DHCP
è
8.2 Dynamic addressing via DHCP server. Alternatively, a static IP address can
be assigned
è
8.2
Dynamic addressing via DHCP server
The automatic assignment of an IP address (DHCP) can be set via the FFT.
1. Connect the bus node with LAN.
2. Install and start the FFT on a Personal Computer.
3. If the device search does not start independently:
Call up the FFT function "Search for devices".
Devices available in the LAN are displayed.
4. If the PC is not in the same LAN sub-network
è
Online help or description of
"FFT".
5. Select the bus node CTEU-VN.
6. In the network settings or using the command line mode, activate the auto-
matic assignment of an IP address (DHCP).
7. Switch bus node off and back on.
The IP address is assigned automatically.
The assignment of an IP address via DHCP can take several seconds. Until a
DHCP address has been successfully assigned, the address 0.0.0.0 is dis-
played in the FFT. If necessary, call up the FFT function "Search for devices"
again
è
Point 3.
8. Call up the FFT function "Search for devices" again.
Devices available in the LAN are displayed.
9. Select the bus node CTEU-VN.
Then carry out the Firmware update
è
Online help or description of "FFT".
8.3
Static addressing
•
Observe the basic addressing rules for the allocation of the IP address, e.g.
with respect to the use of private or public address ranges.
•
Check that the IP address can be used in the network.
•
Ensure that IP addresses are not used more than once.
The allocation of a static IP address can be adjusted via the FFT.
























