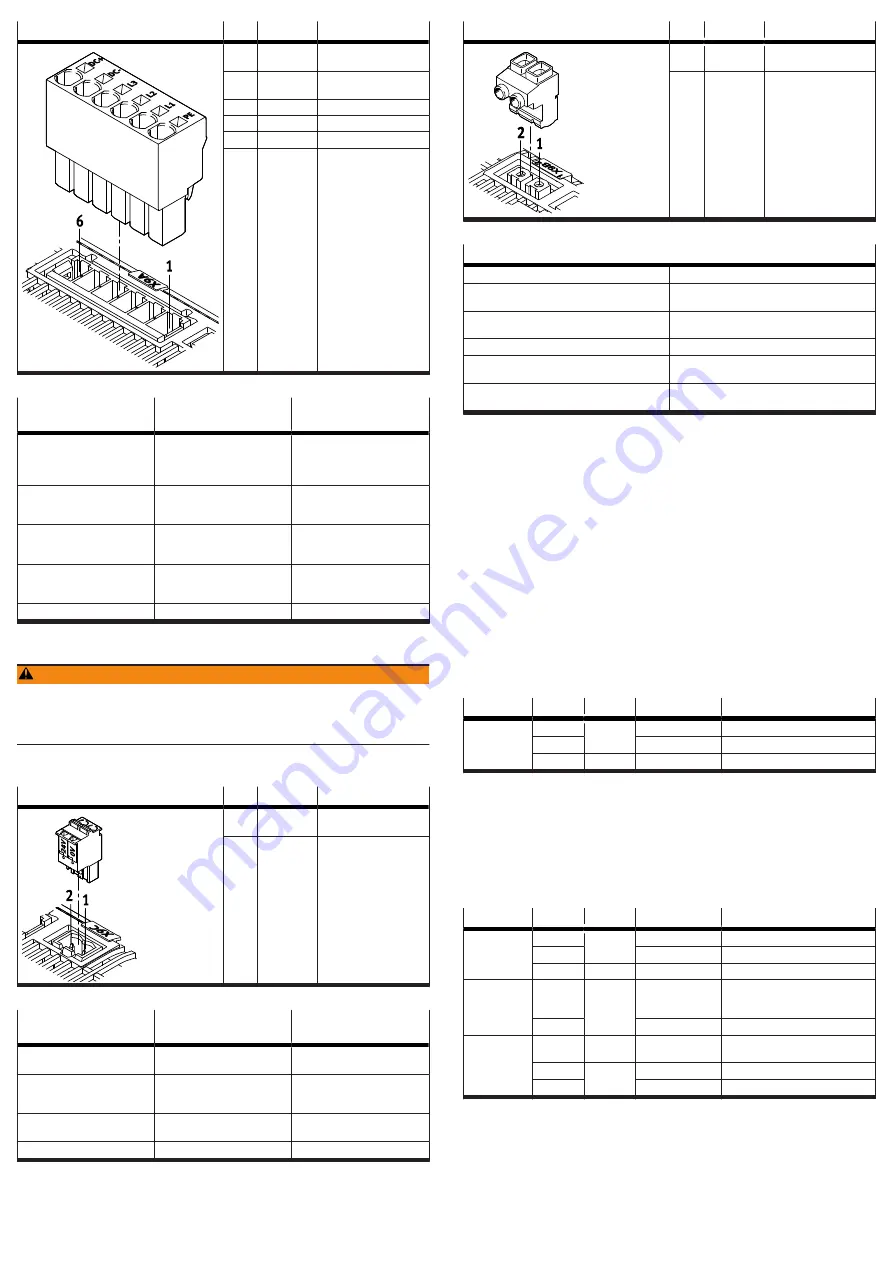
[X9A]
Pin
Function
Description
6
DC+
DC link circuit positive
potential
5
DC-
DC link circuit negative
potential
4
L3
Mains supply phase L3
3
L2
Mains supply phase L2
2
L1
Mains supply phase L1
1
PE
Protective earthing
Tab. 37: Power supply and DC link circuit
Requirements for the
connecting cable
Single device
Device compound
Number of insulated wires and
shielding
4 insulated wires, unshielded
without DC link coupling:
4 wires, unshielded
with DC link coupling: 6 wires,
unshielded
Min. conductor cross section
including wire end sleeve with
plastic sleeve
0.5 mm
2
1.5 mm
2
Max. conductor cross section
including wire end sleeve with
plastic sleeve
4 mm
2
4 mm
2
Max. conductor cross section
including wire end sleeve
without plastic sleeve
6 mm
2
6 mm
2
Max. length
2 m
£
0.5 m
Tab. 38: Requirements for the connecting cable
7.10.2
[X9C], logic voltage supply
WARNING
Risk of injury due to electric shock.
• For the electrical power supply with extra-low voltages, use only PELV circuits
that guarantee a reinforced isolation from the mains network.
• Observe IEC 60204-1/EN 60204-1.
•
Only connect PELV circuits with an output current of max. 25 A. Otherwise,
use a separate external fuse: 25 A.
[X9C]
Pin
Function
Description
2
24 V DC
positive potential of logic
voltage supply
1
0 V
Reference potential for
logic voltage supply
Tab. 39: Logic voltage supply
Requirements for the
connecting cable
Single device
Device compound
Number of insulated wires and
shielding
2 insulated wires, unshielded
2 insulated wires, unshielded
Min. conductor cross section
incl. wire end sleeve with
plastic sleeve
0.5 mm
2
0.5 mm
2
Max. conductor cross section
incl. plastic wire end sleeve
2.5 mm
2
2.5 mm
2
Max. length
2 m
0.5 m
Tab. 40: Requirements for the connecting cable
7.10.3
[X9B], connection for braking resistor
The connection [X9B] is located on the top of the device. The internal braking
resistor or a suitable external braking resistor is attached to the connection [X9B].
[X9B]
Pin
Function
Description
2
BR+Ch
Braking resistor positive
connection
1
BR-Ch
Braking resistor negative
connection
Tab. 41: Connection for the braking resistor
Requirements for the connecting cables of external braking resistors
Number of insulated wires and shielding
2 wires, shielded
Min. conductor cross section incl. wire end
sleeve with plastic sleeve
0.25 mm
2
Max. conductor cross section incl. plastic wire
end sleeve
2.5 mm
2
Max. cable length
2 m
Wiring
inside the control cabinet, shield connected to
PE
Tightening torque of the screw terminals on the
mating plug GIC 2.5 HCV/2-ST-7.62
0.5 … 0.6 Nm
1)
1) Specification of the manufacturer at the time the documentation was approved
Tab. 42: Requirements for the connecting cable
Selection of suitable braking resistors
Information on selecting suitable braking resistors
è
Manual Assembly, Installa-
tion.
7.11
Cross-wiring
Cross-wiring makes it possible to set up a device compound consisting of up to 10
servo drives CMMT-AS. The different cross-wiring options are as follows:
–
Cross-wiring of I/O signals at the connection [X1A]
–
Cross-wiring of the mains and logic voltage supply without DC link coupling
–
Cross-wiring of the mains and logic voltage supply with DC link coupling
Information on cross-wiring
è
Manual Assembly, Installation and Manual Safety
sub-function.
7.12
STO installation
Inputs and outputs for the safety sub-function STO
The 2-channel request for the safety sub-function is made via the digital inputs
#STO-A and #STO-B. The STA diagnostic output indicates whether the safe status
has been reached for the safety sub-function STO.
Connection Pin
Type
Identifier
Function
[X1A]
X1A.11
DIN
#STO-B
Safe torque off, channel B
X1A.12
#STO-A
Safe torque off, channel A
X1A.22
DOUT
STA
Safe torque off acknowledge
Tab. 43: Inputs and outputs for the safety sub-function STO
7.13
SBC installation
Inputs and outputs for the safety sub-function SBC
The 2-channel request for the safety sub-function is made via the digital inputs
#SBC-A and #SBC-B at the connection [X1A]. The SBA diagnostic output indicates
whether the safe status has been reached for the safety sub-function SBC. The
holding brake is connected via the connection [X6B]. The external clamping unit is
connected via the connection [X1C].
Connection Pin
Type
Identifier
Function
[X1A]
X1A.9
DIN
#SBC-B
Safe brake control, channel B
X1A.10
#SBC-A
Safe brake control, channel A
X1A.21
DOUT
SBA
Safe brake control acknowledge
[X1C]
X1C.1
DOUT
BR-EXT
Output for connection of an
external clamping unit (high-side
switch)
X1C.5
GND
Reference potential (ground)
[X6B]
X6B.1
–
FE
Functional earth connected to pro-
tective earth
X6B.2
OUT
BR+
Holding brake (positive potential)
X6B.3
BR–
Holding brake (negative potential)
Tab. 44: Inputs and outputs for the SBC safety sub-function
7.14
SS1 installation
Inputs and outputs for the safety sub-function SS1
The safety sub-function SS1 is wired like the safety sub-function STO but is
supplemented by the functional input CTRL-EN so that the braking ramp can be
activated by the safety relay unit.


































