CAP-835
24
4.2 Brief description
The fresh air supplied by the installed cooling air
fan is filtered through the intake filter. The air
flows through the intake valve into the
compressor airend, where it is compressed
together with the injected oil to the final
pressure. The oil is largely separated from the
compressed air in the oil separator tank. The
air/oil separator removes the remaining oil from
the compressed air. The compressed air then
flows through the minimum pressure and non-
return valve into the air after-cooler and is
cooled down before it leaves the screw
compressor via the discharge port.
The oil is separated from the compressed air in
the oil separator tank and the air/oil separator
and flows to the oil cooler. The oil temperature
thermostat adds the cooled oil to the hot oil via
the oil cooler bypass according to the set point
temperature. Finally, the oil filter cleans the oil
before it is injected into the compressor airend
again.
4.3 Assembly description
4.3.1
Enclosure doors
Only qualified personnel may remove the
enclosure doors with the included special
wrench. Enclosure doors are a part of the
electric shock protection and reduce the sound
level emitted by the unit.
4.3.2
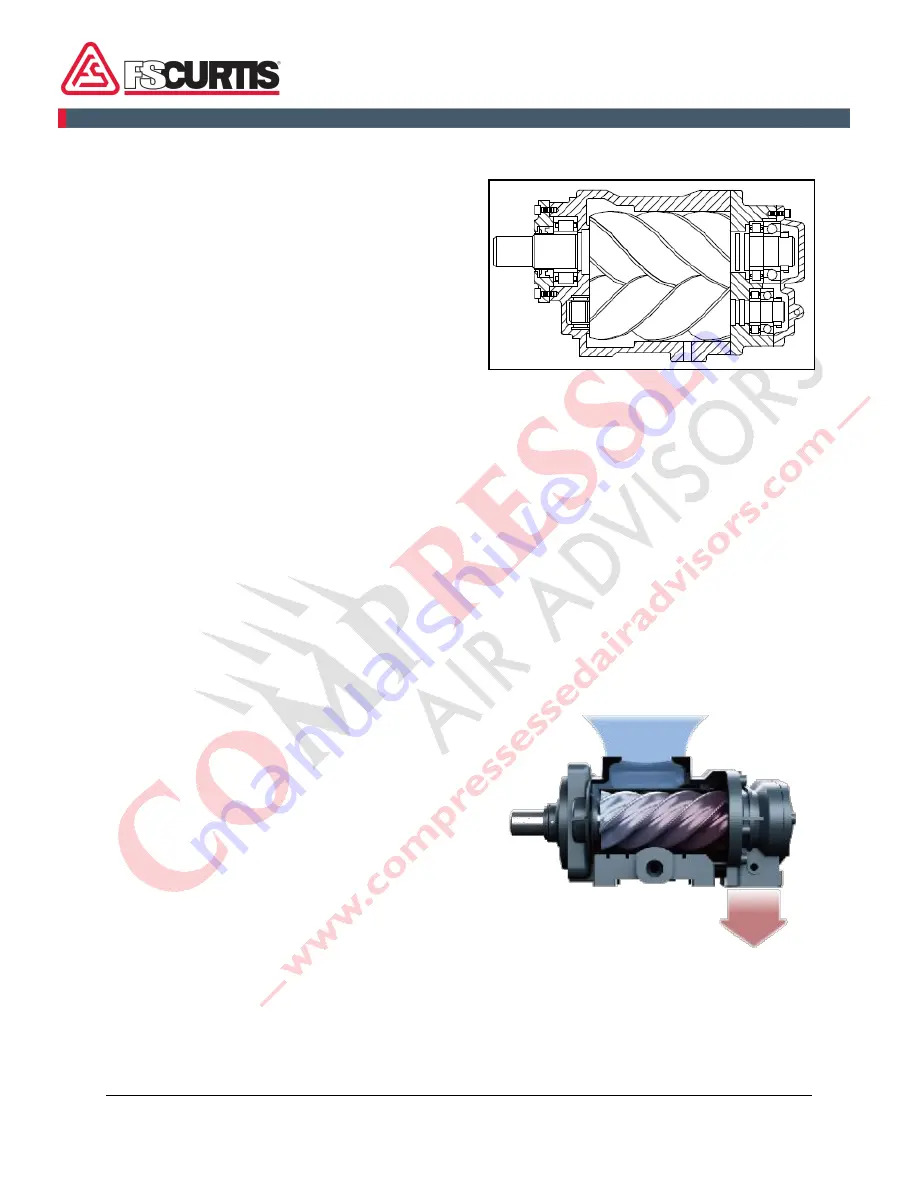
Screw Compressor
The compressor assembly is an oil flooded
positive displacement, single stage, helical
screw type unit consisting of two rotors or
screws supported axially by roller bearings and
enclosed in a housing or stator as depicted in
the sectional view.
4.3.2.1
Drive unit
Belt and direct drive units are installed in the
screw compressors. They differ in construction,
their technical data and their functional principle
as follows:
In operation as depicted above in the compression
cycle, air entering the compressor through the inlet
port becomes trapped between the helical lobes of
the main rotor and the matching grooves of the
secondary rotor. As the rotors turn air is trapped in the
cavity created by the meshing lobe and groove and
reduced in volume or “compressed”. It is then pushed
through the successive cavities until it reaches the
discharge end of the compressor and is sent to the oil
separator.
During the compressor cycle, oil is injected into the
compressor for the purpose of dissipating the heat of
compression and to seal the internal clearances. The
compressed air laden with oil leaves the compressor
through the discharge port and enters a reservoir
where the oil and air are separated. This process
delivers a smooth flow of compressed air at the
desired pressure.
















































