If the scale selected is 'MIDI 1' or 'MIDI 2' (values 17 & 18) the candidate notes for quantization are
set via MIDI. The algorithm listens for MIDI note on messages and uses the received notes for the
quantization pattern. While any notes are held, playing new notes adds to the pattern. When all
notes are released and a new note played, the pattern is reset and formed from the new note.
In 'MIDI 1' mode the played MIDI notes set the note names, but quantization can happen in any
octave (i.e. if you play a 'D' the output will always be 'D' but the octave will depend on the octave of
the incoming CV).
In 'MIDI 2' mode the played MIDI notes are the only ones that can be output (so say if you play
middle C and the D above, the output will always be one of those two notes, depending on whether
the input CV is below or above middle C).
Parameter 5 sets an offset between the timing of the Z input vs the X & Y inputs (in sample
frames). When using Z as a trigger, it is often a good idea to delay it slightly relative to the pitch, to
ensure that the pitch has changed and settled before the trigger samples a new note.
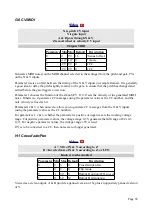
Parameter 6 sets the root
key
of the chosen scale. At zero, the first note of the scale (e.g. C in the
key of C) corresponds to 0V. If the parameter is set for example to 2, the first note of the scale is at
2/12 = 0.1667V - or to look at it another way, if your VCO is tuned so that 0V gives you a C, the
quantizer is now working in the key of D (D major, minor, triad etc. depending on the scale setting).
The quantized notes names are shown on the display (A left, B right). Natural notes are shown in
capitals i.e. 'C', 'D', 'E' etc. Lower case letters indicate sharps e.g. 'c' indicates C sharp, 'd', indicates
D sharp.
MIDI Output
: each new note is output as a MIDI note message on the MIDI channel selected in
the settings (input X/output A) or on the next highest channel (input Y/output B). E.g. if the settings
specify MIDI channel 4, the notes are output on channels 4 (X/A) and 5 (Y/B).
The MIDI Gate parameter works in the same way as for the Quantizer, above.
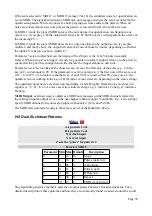
H-5 Dual Euclidean Patterns
A is pattern 1 out
B is pattern 2 out
X is clock input
Y is reset input
Z sets the 'pulses' for pattern 2
Receives MIDI
Parameter Min Max Default
Description
0
1
16
16
Steps.
1
1
16
4
Pulses (pattern 1).
2
0
96
0
A Rotation.
3
0
31
0
Pulse length.
4
-1
96
-1
B Rotation.
5
0
96
0
Repeat.
6
-15 15
0
MIDI clock divisor.
This algorithm generates rhythmic patterns of output pulses known as Euclidean patterns. For a
detailed description of these patterns and how they are commonly found in music around the world
Page 70