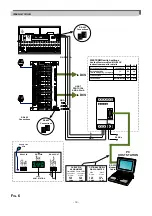
- 29 -
12.6 MUX 1700 Differences
Most of the previous considerations still apply to the MUX 1700 Hart multiplexer solution, the design of which is
very similar to the 2700 version. However, some differences are to be taken into account, which is listed in the fol-
lowing.
• Polarised input capacitor
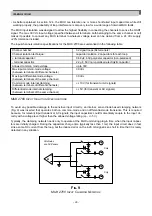
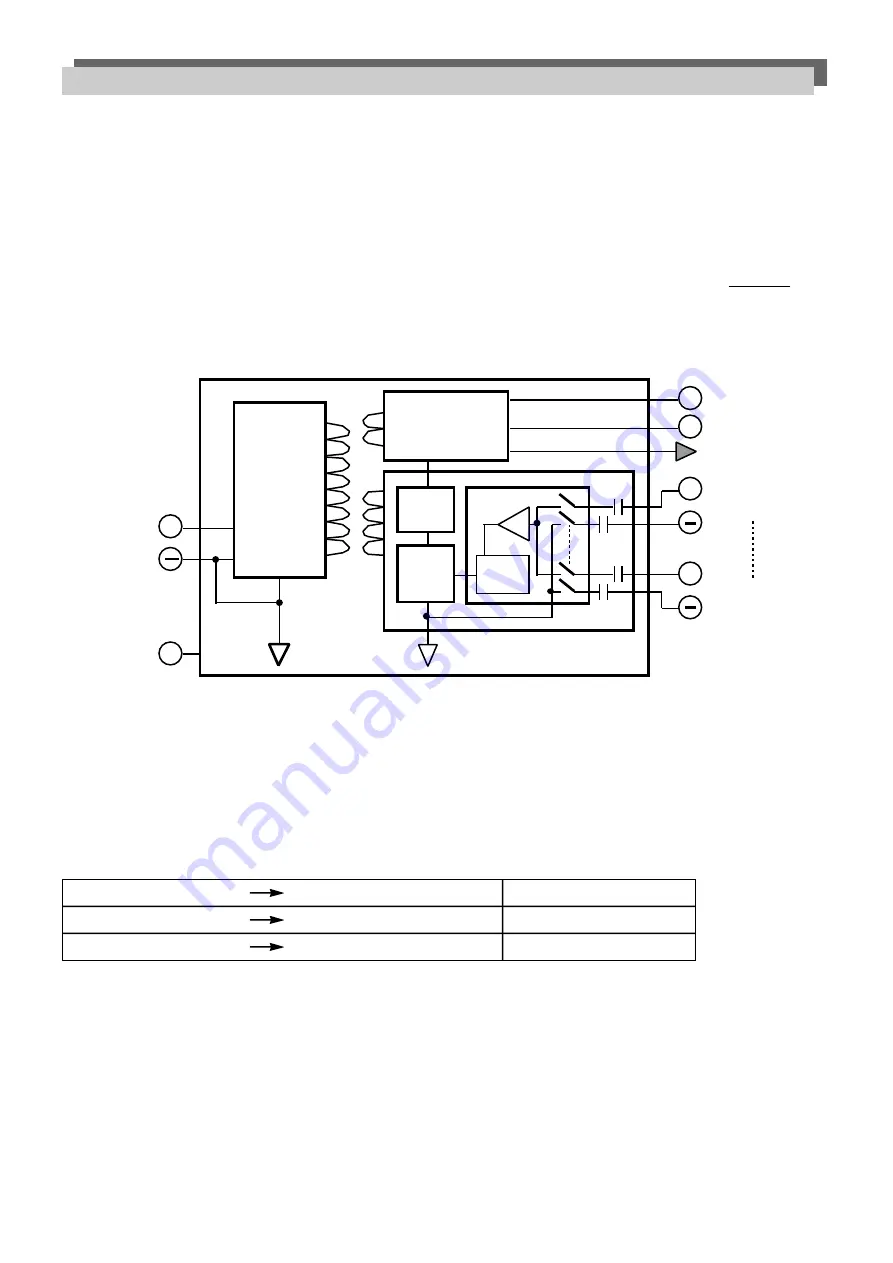
As can be seen in fig 11, the MUX 1700 input capacitor associated with the – terminals is of the polarised type.
Therefore, the application must be designed so that it is not possible, for any – terminal, to go to an higher DC
potential than that any + terminal. If this is not the case, the capacitor on the – terminal could be reverse polari-
sed and could fail (also if, in the short term, it would appear to work properly).
• Isolation specifications
The galvanic isolation specifications for the MUX 1700 are not as good as the MUX 2700, however this is not
likely to be a problem in almost all the applications
The galvanic isolation specifications for the MUX 1700 are summarised in the following table:
IM-ENG-116/GB
POWER
SUPPLY
UNIT
+
24V
RS-485
INTERFACE
OPTO
ISOL.
CPU
MUX
A
HART
MODEM
+
+
A1
A3
SCREEN
A4,A5,A6
A31
A
A30
B
A32
10µF
1µF
10µF
1.5µF
C32
B32
C1
B1
CH1
CH32
+
+
F
IG
. 11
MUX 1700 I
SOLATION
S
TRUCTURE
24V supply
Field channels
500 Vac, rms
24V supply
RS-485 serial port
500 Vac, rms
RS-485 serial port
Field channels
250 Vac, rms
MUX 1700 G
ALVANIC
I
SOLATION
S
PECIFICATIONS
• Input capacitors values
The MUX 1700 input capacitors value are larger than the MUX 2700. This has some advantage as for HART
signal levels, but results in a longer capacitor charge time when a unit is plugged-in. However the charging time,
typically < 2ms, is not such to induce any relevant error signal error in most situations.