13
EATON
LifeSense Wireless System Quick Setup Guide E-HOOV-II002-E July 2014
Note:
Be sure to have gathered the information listed in the
Internet setup portion of the Wireless Setup Information
Form. The NIST and DNS IP addresses as well as the network
information needed for the internet connection is critical for
the upcoming steps.
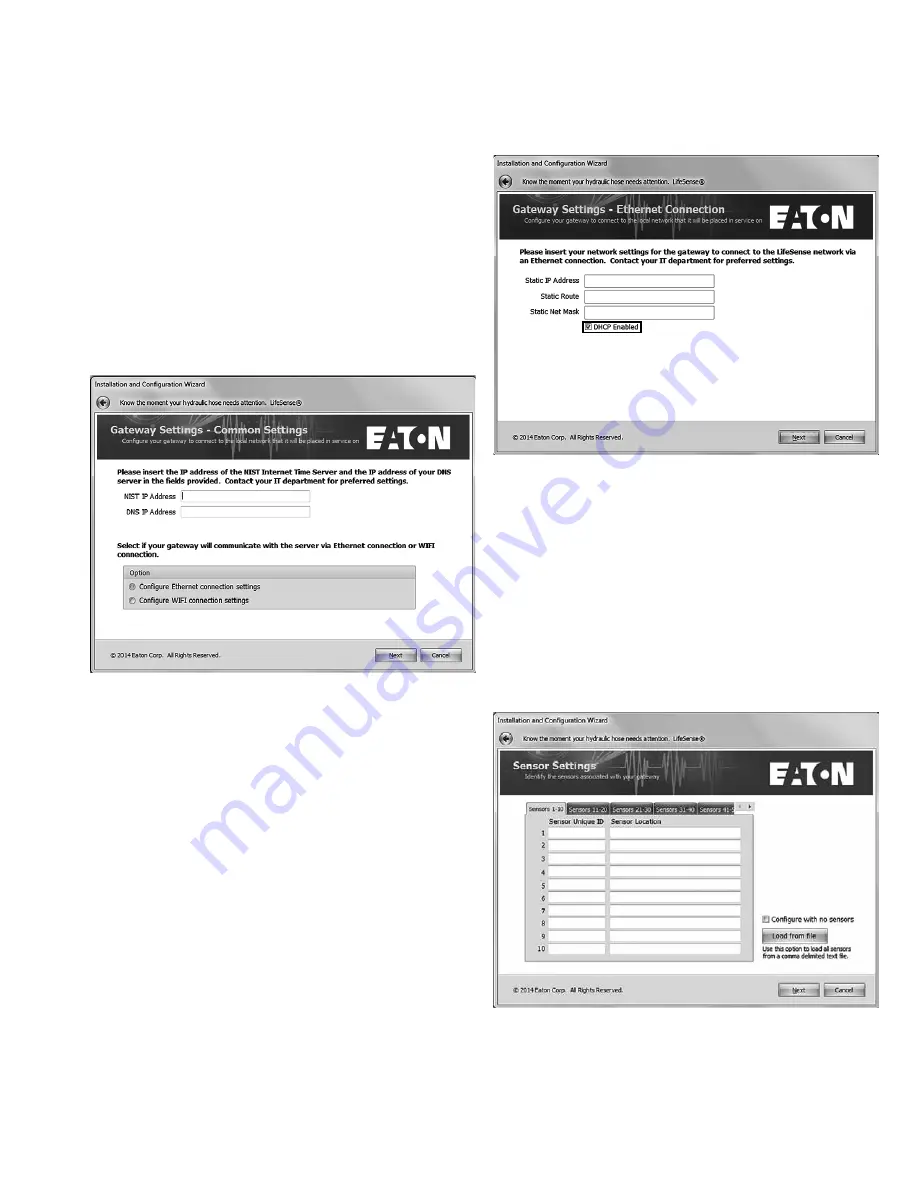
In this series of screens you will be entering the network
address information for which the wireless gateway (HDU)
will be configured to transmit data to the server on which the
LifeSense customer web portal resides.
Input the NIST and DNS IP addresses that will be used on the
network and then select if the wireless gateway (HDU) will be
connecting to the Internet via Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
Click Next.
Note:
DHCP is usable; however, if a company wants to
assign a static IP address to the wireless gateway (HDU) this
information will need to be acquired from the company’s IT
department.
Configuring Ethernet Connection
Select DHCP or enter the static IP address, route, net mask
and Wi-Fi net mode assigned.
Click Next.
Sensor Settings
Each wireless LifeSense sensor has a ten digit unique
identification number located on the top of the sensor. This is
so you will know exactly which sensor within the LifeSense
system is issuing an alert. It’s in the Sensor Settings screen
where you will input each sensor ID, either manually, or by
loading them from a comma delimited file.
Manual Input
Type the unique sensor ID in the given field, then tab over to
the Sensor Location field, and type in a description of where
the hose assembly is located on the equipment. When all
sensors have been inputted click Next.
Loading from a File
If you are loading the sensors from a file click on the “Load
from file” button which will bring up a screen from which you
can select a comma delimited file on your computer, or on
an external storage device connected to your computer (e.g.,
Wireless Gateway (HDU)
Configuration
(LifeSense Installation Wizard)























