Chapter One
Introduction
Man_455U-D Rev 3.07
Page
17
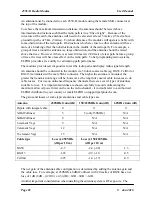
The time taken to transmit a message is :-
Section
Item
Number
Time (At 9600 Baud)
PEAMBLE
Lead-in
40 msec Default
(Configurable)
40 msec
HEADER
System Address
2 Bytes
2.08 msec
Header Control
2 Bytes
2.08 msec
Source Address
1 Byte
1.04 msec
Destination Address
1 Byte
1.04 msec
Intermediate Address 1 Byte per address
1.04 msec for each address
Header Error Check
1 Byte
1.04 msec
ENCRYPTION Initialisation Vector
16 Bytes (if enabled)
16.64 msec (If configured)
DATA
Message Data
Data Bytes
1.04 msec x no of data bytes
CHECK
CRC Error Check
2 bytes (if enabled)
2.08 msec (If CRC configured).
The time for each byte is 1.04msec @9600 bits/sec, 2.08 msec at 4800 bits/sec, and 4.16 msec
at 2400 bits/sec.. If error checking is not configured at the receiving unit, data will start to be
output immediately after the first data byte has been received. If error checking is configured,
data will be output approx 1msec after the end of the message. For example, a message with
20 bytes of data transmitted at 9600 bits/sec with no repeaters, will start to be output approx
71msec after the data is input, if error checking is configured, and will start to be output
approx 47 msec after the data is input if no error checking is configured.
A “transmit delay” time and a “receive delay” time may also be configured. These parameters
may be used to fine tune and give priority to different 455U-D units in a system.
After each message is transmitted, a 455U-D unit will not transmit another message during
the transmit delay time. This could be used to allow a reply message to be received before
the next message is sent.
After a message is received, a message will not be transmitted during the receive delay time.
This could be used to delay a reply message until other messages have been sent.
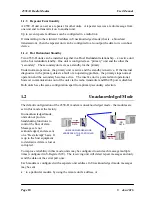
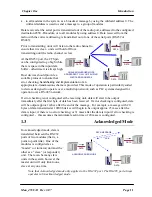
1.6
Addressing
A 455U-D network comprises modules with the same "system" address. Only modules with
the same system address will communicate with each other. This feature allows more than one
system to operate in the same area on the same radio channel.
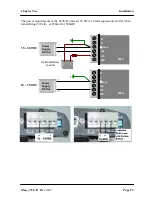
A 455U-D must also be configured with a “unit” address - this gives the module a unique
identification. The unit address is used to identify the two data ports on each 455U-D. The
RS232 port is accessed by addressing the configured unit address. The RS485 port is accessed
by addressing the configured unit a128. So, to access the RS232 port on unit 7, use
address 7. To access the RS485 port on this unit, use address 135 (128+7).
Addresses 0 and 128 are reserved as “wildcard” addresses. Sending a message to address 0
results in all modules accepting the message. Address 0 refers to every RS232 port in the
system. Address 128 is the wildcard address for every RS485 port in the system.