Air ionization can neutralize the
static charge on insulated and
isolated objects by producing
separate charges in the molecules of
the gases of the surrounding air.
When an electrostatic charge is
present on objects in the work
environment, it will be neutralized
by attracting opposite polarity
charges from the ionized air. Note
that ionization systems should not be
used as a primary means of charge
control on conductors or people.
(Reference: IEC 61340-5-2:1
paragraph 5.2.9).
The Desco EMIT’s Critical
Environment overhead ionizers are
NIST calibrated and are available in
four models:
The 50606 and 50608 are 24" long
units with 2 fans, and the 50607 and
50609 are 48" long units with 4 fans.
All models have the same features
permitting the user to select the best
size for the application. Since our
introduction of the first overhead
ionizer in the market, we have
continued to enhance our offerings
with the most advanced features
available.
TB-6529
Page 2 of 9
Description
Ionizers are useful in preventing
electrostatic charge generation,
ElectroStatic Discharge,
ElectroStatic Attraction, as well as
preventing equipment latch-up and
safety related shock. ANSI/ESD
S20.20 Paragraph 6.2.3.1 Protected
Areas Requirement states:
"Ionization or other charge
mitigating techniques shall be used
at the workstation to neutralize
electrostatic fields on all process
essential insulators if the
electrostatic field is considered a
threat." Ionization is used to
neutralize charges on process
necessary insulators and isolated
semiconductors. Some examples of
process necessary insulators are: the
PC board itself, plastic test stands,
plastic housing where a PCB may be
mounted, as well as computer
monitor screens and regular cleaning
wipes. Examples of floating or
isolated conductors are: loaded PCB
mounted in a stand where the pins
are not contacting the dissipative
workstation. Ionization is not
effective on items that have large
capacitance, like people and carts;
however, ionizers should be
considered as a method for charge
neutralization in cases where
grounding cannot be achieved.
IONIZER SELECTION
ANSI/ESD S20.20 paragraph
6.1.1.2. ESD Control Program Plan
Guidance states: "The Plan should
include a listing of the specific type
of ESD protective materials and
equipment used in the Program."
When selecting an ionizer life cycle
costs should be considered
including: equipment cost;
installation cost; and operation and
maintenance cost.
The C/E series offers many design
improvements, most notably, our
patent-pending “Emitter Cassette”
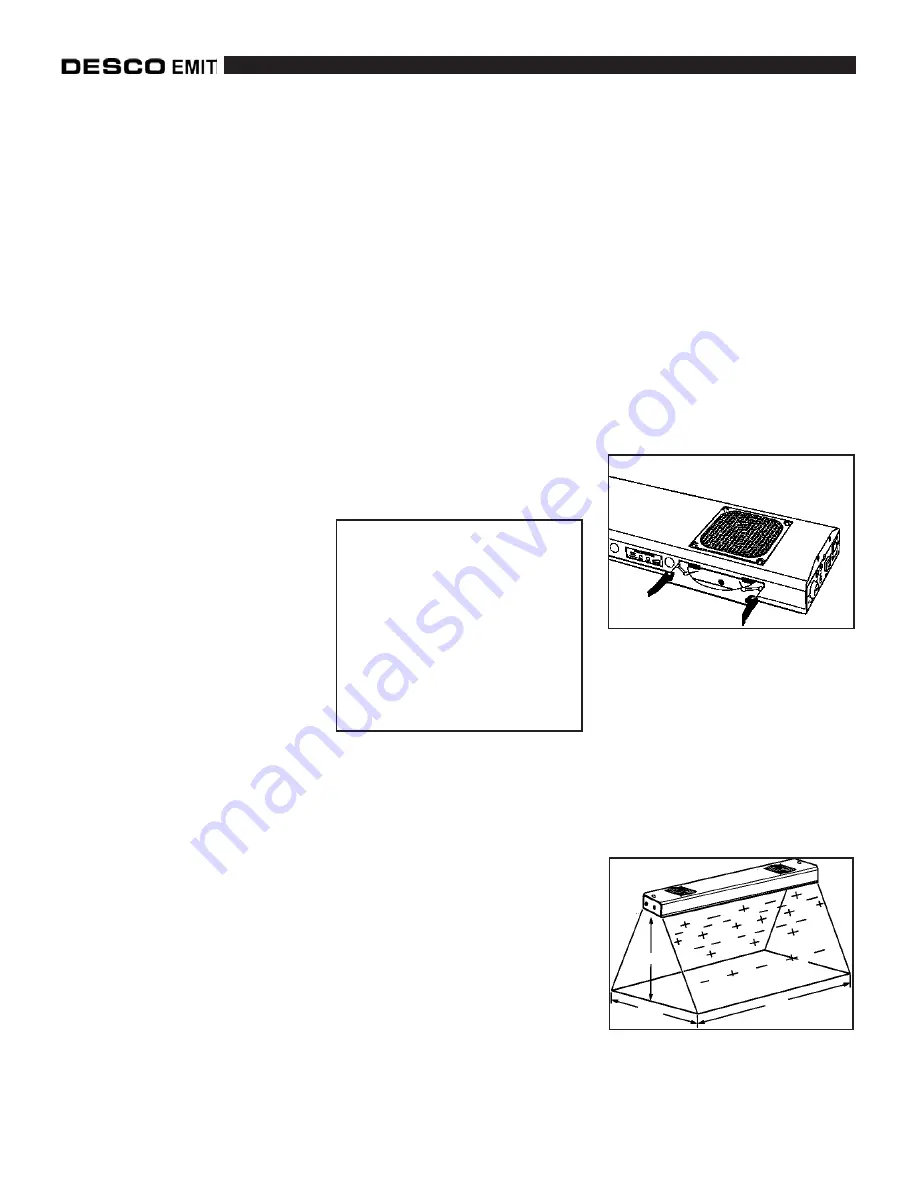
(see figure 1).
Figure 1. Removable emitter
cassette
While other manufacturers attempt
to simplify or automate the cleaning
of the emitter pins, what remains is
one major flaw in the process -
unless the ionizer is removed to
another area, the contamination ends
up on the workstation and on any
product that happens to be nearby.
Figure 2. Area of optimum charge
neutralization for 50606 and 50608
50606
C/E Ionizer 24", 120 Volt
50607
C/E Ionizer 48", 120 Volt
50608
C/E Ionizer 24", 220 Volt
50609
C/E Ionizer 48", 220 Volt
*U.S. Patent #6,137,670
24 IN.
24 IN.
30 IN.
OPTIMUM
PERFORMANCE ZONE
© 2007 DESCO INDUSTRIES INC.
Employee Owned









