Configuration
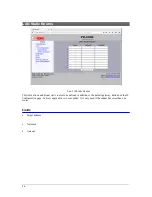
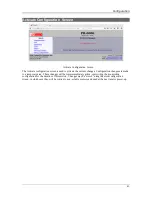
Replication Statistics Screen
Replication Statistics Screen
The Replication Statistics Screen shows the number of hits attributed to each replication rule. It also
displays the latest Address Resolution (ARP) Table. The ARP table may time out, but is useful to diagnose
problems caused by non-responding IP addresses.
Rule Hit Count – This metric counts the number Ethernet packets that have matched the corresponding
rule. This counter is 32-bits so will eventually roll over.
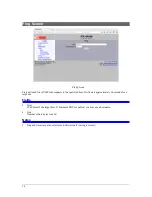
Rule 1-sec Rate – This metric counts the number of Ethernet packets that have matched the corresponding
rule over the last 1 second period. It provides a snapshot of current activity.
Rule Peak Rate – This metric records the highest 1-second rate. It is useful in trouble-shooting conditions
that may be overloading the Packet Repeater.
Address Resolution Hit Count – This metrics counts the number of times the Packet Repeater has directed
a packet to a specific IP address.
Address Resolution Drop Count – When the Packet Repeater needs to resolve an address, it will buffer a
small number of Ethernet packets, pending resolution. The Drop Count is the number of Ethernet packets
dropped because the address had not yet resolved.
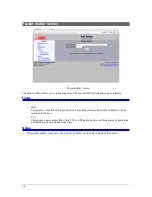
I/O Statistics Rx Total – This metric counts the number of incoming Ethernet packets analyzed by the
Packet Repeater. This counter is 32-bits so will eventually roll over.
I/O Statistics Rx Overrun – This metric counts the number of packets that the Packet Repeater dropped
because it could not keep up with the incoming Ethernet packets. This is the primary indicator that the
Packet Repeater has been overloaded.
I/O Statistics Rx 1-sec PPS – This metric counts the number of incoming Ethernet packets analyzed over
the last 1 second period. It provides a snapshot of current activity.
I/O Statistics Rx Peak PPS – This metric records the highest 1-sec PPS rate. It is useful in trouble-shooting
overload condition.
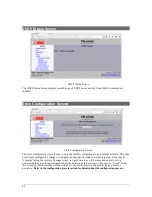
I/O Statistics Tx Total – This metric counts the number of Ethernet packets generated and output by the
Packet Repeater. This counter is 32-bits so will eventually roll over.
I/O Statistics Tx Overrun – This metric counts the number of Ethernet packets dropped because the
Ethernet transmit queue was full. This metric is an indication that too many packets are being generated by
39