PCI-PID01 User‟s Manual
3
1. PID Control Concept
Proportional-Integral-Derivative controller (PID controller) is the typical form of the control scheme
and most commonly used in real applications. PID controller basically has the
type, measure the output that you want to control the target, calculate the error that you want to
compare with set value or reference value, this error value is used to calculate the values needed to
control structure.
P
K
p
·e(t)
I
K
i
·
∫ e(t)dt
D
K
d
·de(t)/dt
0
t
∑
∑
error
output
Set
Point
-
+
process
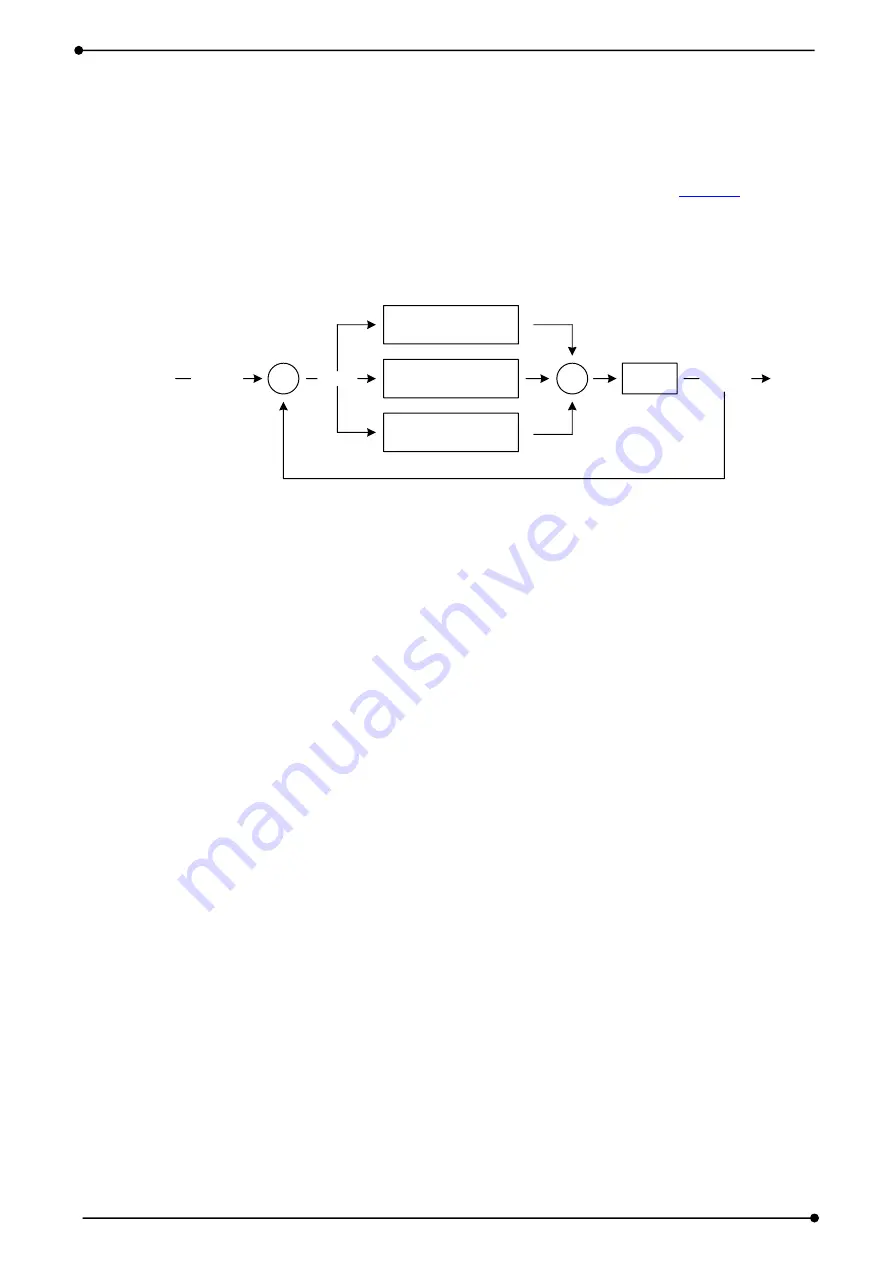
[Figure 1-1. PID Control Structure]
Standard form of PID controller is configured to calculate the control value (MV : manipulated
variable) by adding three item of following expression.
MV(t) = K
p
·e(t) + K
i
·
∫ e(t)dt + K
d
·de(t)/dt
0
t
PID(Proportional–Integral–Derivative controller) that has a name because this item is proportional
to their error value, the integral of error value, the derivative of error value. Three items meanings
are as follows.
Proportional : Control action that is proportional to the size of error value in the current state
Integral : Acting to eliminate steady-state error value.
Derivative : Braking to a sudden change of the output, reduce overshoot and improves stability.
PID controller is used above standard form. But in some case, there are many methods to use
slightly modified form. For example, simplify the use of the controller with proportional item, or
proportional-integral item, or proportional-derivative item. In this case, each of P, PI, PD is called.
The control parameter
K
p
,
K
i
,
K
d
is called a gain value or gain, Tuning is called the process of
mathematical or experimental/empirical method to calculate the appropriate gain.
PID controller is used to measure the reaction of the automation system, as well as to control the
reaction, in order to control the temperature, pressure, flow rate, rotation speed, etc.




































