DGS-1024T Unmanaged Gigabit Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
2
Switching Technology
Another key development pushing the limits of Ethernet technology is in the field of
switching technology. A switch bridges Ethernet packets at the MAC address level of the
Ethernet protocol transmitting among connected Ethernet or fast Ethernet LAN segments.
Switching is a cost-effective way of increasing the total network capacity available to users
on a local area network. A switch increases capacity and decreases network loading by
making it possible for a local area network to be divided into different segments which don’t
compete with each other for network transmission capacity, giving a decreased load on
each.
The switch acts as a high-speed selective bridge between the individual segments. Traffic
that needs to go from one segment to another (from one port to another) is automatically
forwarded by the switch, without interfering with any other segments (ports). This allows
the total network capacity to be multiplied, while still maintaining the same network
cabling and adapter cards.
For Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet networks, a switch is an effective way of eliminating
problems of chaining hubs beyond the “two-repeater limit.” A switch can be used to split
parts of the network into different collision domains, for example, making it possible to
expand your Fast Ethernet network beyond the 205-meter network diameter limit for
100BASE-TX networks. Switches supporting both traditional 10Mbps Ethernet and
100Mbps Fast Ethernet are also ideal for bridging between existing 10Mbps networks and
new 100Mbps networks.
Switching LAN technology is a marked improvement over the previous generation of
network bridges, which were characterized by higher latencies. Routers have also been
used to segment local area networks, but the cost of a router and the setup and
maintenance required make routers relatively impractical. Today’s switches are an ideal
solution to most kinds of local area network congestion problems.
DGS-1024T Gigabit Ethernet Switch
General Description of Switch
The D-Link’s new unmanaged the DGS-1024T provides 22 1000BASE-T copper ports and 2
Combo (1000BASE-T/Mini-GBIC) ports. Each all-gigabit-port switch is designed for
backbone and server connection with department and enterprise networks. Powerful and
versatile, they eliminate network bottlenecks while giving users the capability to fine-tune
performance.
As Layer 2 switches, all ports of the DGS-1024T provide wire-speed switching by hardware-
based ASIC. With a height of 1U and a standard rack-mount size, the switches are
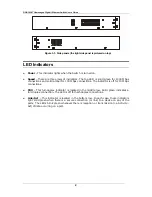
especially suitable for a departmental environment. Clear, at-a-glance per-device/per-port
LED indicators make it easy for users to understand and control network status.
Each of the unmanaged stand-alone switches is equipped with unshielded twisted-pair
(UTP) cable ports providing dedicated 10/100/1000 Mbps bandwidth. DGS-1024T has 22
1000BASE-T copper ports and 2 Combo (1000BASE-T/Mini GBIC) ports. These ports can
be used for connecting network backbones, PCs, and servers. The copper ports use
standard twisted-pair cabling, while the two mini-GBIC ports use fiber optic cabling.