GB
MXV, MXV-B Rev6 - Operating Instructions
Page 17 / 136
Provide space around the pump for motor
ventilation, to allow for checking of shaft rotation,
for filling and draining the pump and to allow for
collection of the liquid to be removed
(especially
for draining liquids which are harmful or have to be
removed at temperatures higher than 60 ˚C).
Make sure prolonged accidental leakage of
liquid does not cause damage to persons
or property.
Leakage may develop as a result of surge pressure or
water hammer, erroneous operations (such as failing
to close a plug or valve) or other functional disorders.
Allow for the possibility of channeling away any leaked
liquid or for an automatic drainage system against
flooding.
Mount the pump on a flat horizontal surface (using a
level gauge) such as a solid cement base or a rigid
supporting structure in metal.
To ensure stability, insert, if necessary, small pieces of
calibrated metal plate next to the 4 anchoring screws.
6.5.
Connecting the motor (only MXV(L),
MXV(L)4)
The
MXV(L), MXV(L)4
pumps are designed for use
with standard electric motors with (IEC 34-7) IM V1
construction form and dimensions and output ratings
in accordance with IEC 72.
If a pump is supplied without the motor
, check the
rated power and rpm indicated on the name plate and
technical data given in the data sheet.
ATTENTION
: the motors must have two lifting points
in diametricalIy opposite positions for vertical lifting
with the shaft end downwards (fig.1 b)
Before installation clean the motor shaft extension, the
key and contact surfaces of the flanges to remove any
protective paint, dirt or oxydation.
Lubricate the motor shaft extension with a graphite-
base, dripfree, anti-friction product.
Do not use oil as it can harm the mechanical seal
below (see
section 8.4.
).
With the pump in the vertical position, insert the motor
shaft in the coupling, aligning the key with the key slot
and resting the motor flange on the lantern flange.
Turn the motor, adjusting the position of the terminal
box as required and aligning the holes on the flanges.
ATTENTION
: the 4 flange screws (70.18) with
nut must be uniformly tightened with alternated
crossover tightening procedure in diametrically
opposite positions (see
section 9.1.
).
Before and after tightening the screws (70.18), make
sure the coupling with pump shaft and motor shaft can
be freely turned by hand (remove and then replace the
guard 32.30).
ATTENTION
: for removing or replacing the motor
see
section 8.3.
6.6. Pipes
Provide a diameter assuring a liquid flow velocity not
higher than 1.5 m/s for suction, and 3 m/s for delivery.
The pipe diameters must never be smaller than the
pump connection ports.
The arrows on the pump casing (14.00) indicate the
inlet (suction) and outlet (delivery) ports.
Ensure the internal pipe surface is clean before
connection.
Secure all pipes to their rests close to the pump and
connect them so that they are not subjected to stress
and do not transmit vibration or flexion strain to the
pump (see
fig.3
).
Provide for the possibility of draining the pump
without having to drain the entire system.
Install correctly any compensators for absorption of
expansion or impeding noise transmission.
Make sure gaskets do not protrude inside the pipes
for the pump types MXV-B, MXV(L) 25,32,40 and
MXV(L)4 25,32,40 screw the union couplings or the
flanges into the
threaded ports
(ISO 228) by inserting
in the joint a suitable sealing material.
Tighten the pipes or union couplings only to the extent
sufficient to ensure a tight seal. Excessive torque may
damage the pump.
With
flanged ports
make sure the gaskets do not
protrude inside the pipes.
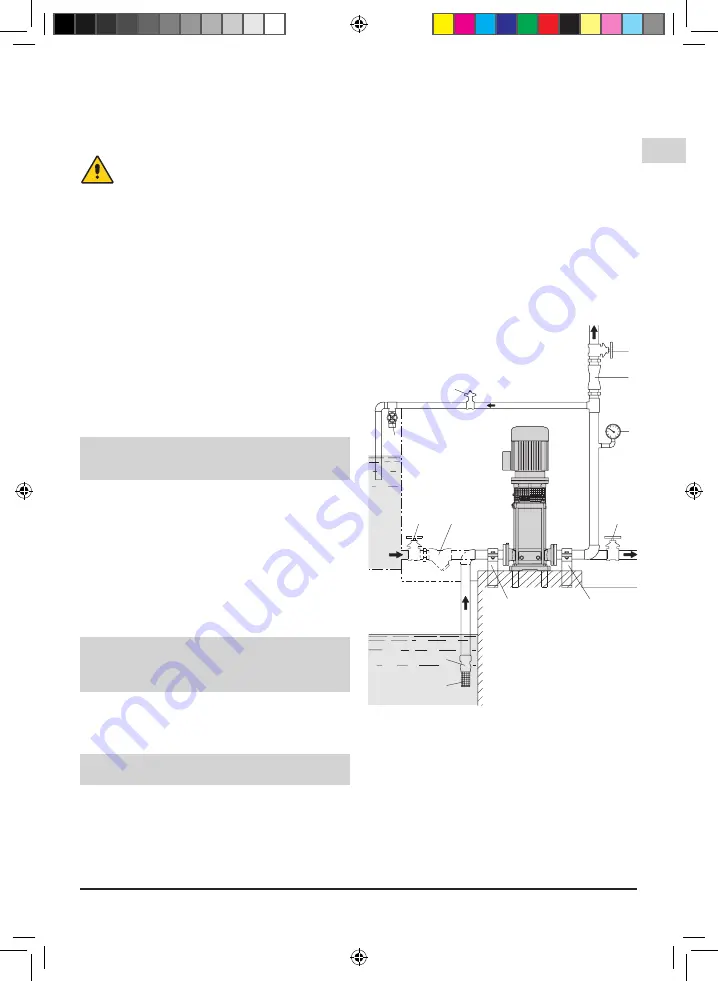
A
B
6
3
5
2
7
4
5
7
1
5
1
5
3.93.113
6.6.1. Suction pipe
When a
pump is located above the water level
(suction lift operation,
fig. 3 A
), fit a foot valve with a
strainer, which must always remain immersed.
The suction pipe must be perfectly airtight and be led
upwards in order to avoid air pockets.
When the
liquid level on the suction side is above
the pump
(inflow under positive suction head,
fig. 3
B
), fit a gate valve.
Follow local specifications if increasing network
pressure.
Install a strainer on the suction side of the pump to
prevent foreign particles from entering the pump.
1. Strainer
2. Foot valve
3. Check valve
4. Bypass valve
5. Gate valve
6. Pressure gauge
7. Supports and clamps for
pipelines
Fig. 3 Systems diagram
A = Suction lift operation
B = Positive suction head operation
MXV, MXV-B Rev6.indd 17
01/10/18 17:06






































