4
Rapid Exhaust
(Figure 8) -
The Rapid Exhaust operation
described in the following text occurs when the modulator is
controlling service chamber(s). During a very rapid brake
release the modulator will exhaust air in a different manner.
An example of this would be the case if the driver made a
severe brake application then lifted his foot from the foot
valve. During a rapid brake release, the rapid return of air
from the brake chamber to the supply port lifts the bias valve
from its normal position. The bias valve orifices the return
air which induces differential pressure across the exhaust
diaphragm. This differential pressure lifts the exhaust
diaphragm from its seat. Returning air flows past the open
exhaust and out the modulator exhaust port.
ANTILOCK OPERATION
GENERAL
If a service brake application is made and the antilock system
detects an impending wheel lockup, the antilock controller
will immediately begin modification of the brake application
using the modulator.
In order to modify the brake application, the coils of the two
solenoid valves contained in the modulator are energized or
de-energized in a preprogrammed sequence by the antilock
controller. When a solenoid coil is energized, and depending
whether the exhaust or hold solenoid is energized, it either
opens or closes, thereby causing the exhaust or
reapplication of air pressure to the brake actuator. The
solenoids in the modulator are controlled independently by
the antilock controller. By opening and closing the solenoid
valves in the modulator, the antilock controller is able to
simulate what the driver does when he pumps the brakes. It
must be remembered, however, that unlike the driver the
antilock controller is able to cycle each modulator, along
with the brakes connected to it, independently and with far
greater speed and accuracy.
ANTILOCK EXHAUST
(FIGURE 9)
When wheel lock is detected or imminent, the antilock
controller simultaneously energizes both the supply and
exhaust solenoids in the modulator. Energizing the supply
solenoid causes its exhaust to close and its inlet to open.
With the inlet of the supply solenoid open, application air is
permitted to flow to the control side of the supply diaphragm.
Air pressure acting on the supply diaphragm causes it to
close the supply and prevent further delivery of air to the
brake chamber.
Energizing the exhaust solenoid closes its inlet and opens
its exhaust. By closing the exhaust solenoid inlet, application
air is prevented from flowing to the control side of the exhaust
diaphragm. Air pressure which was present on the control
side of the exhaust diaphragm flows out the exhaust port of
the modulator. With control air pressure removed from the
exhaust diaphragm, brake application air forces the exhaust
diaphragm to unseat, allowing it to flow out the modulator
exhaust port. The modulator will remain in the antilock
exhaust mode until the antilock controller senses that wheel
speed has increased. The modulator can enter the antilock
hold or reapply mode from the antilock exhaust mode.
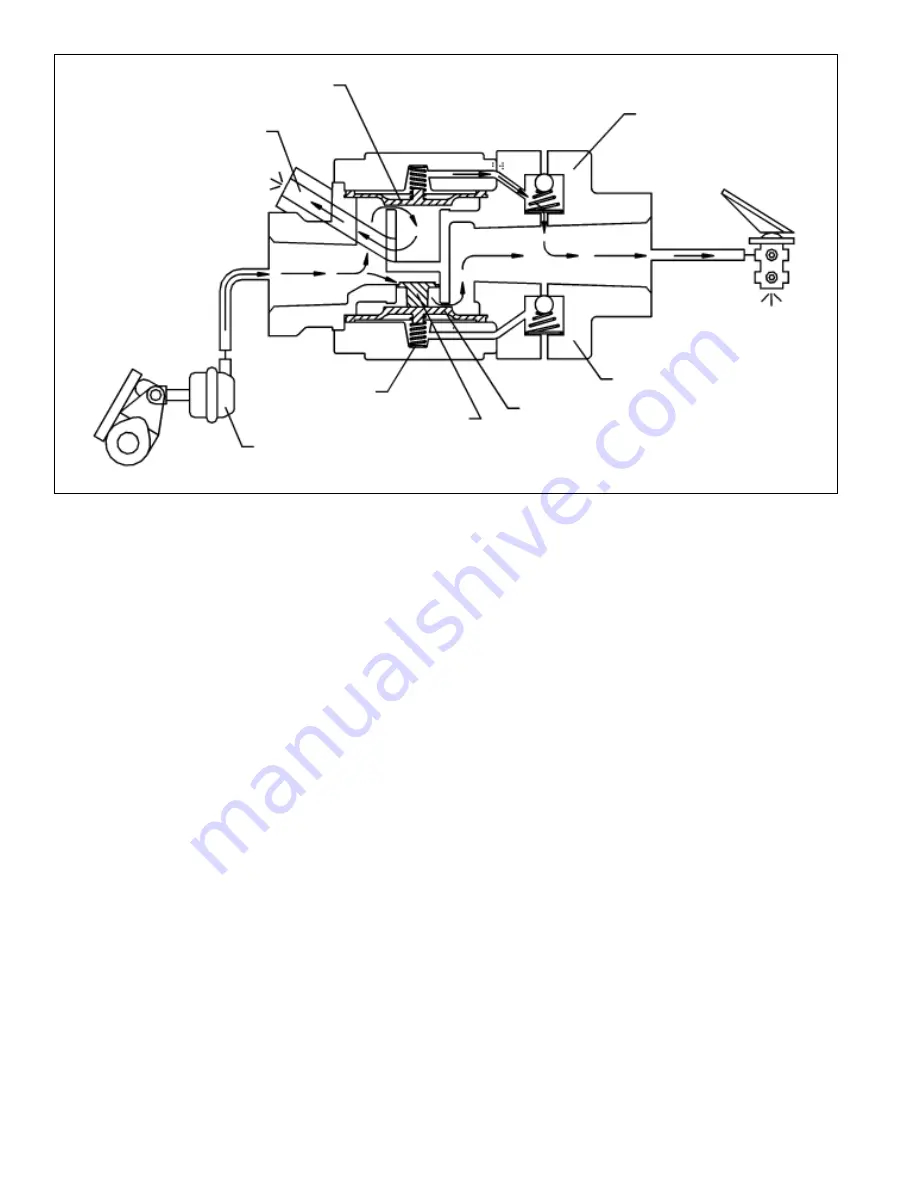
FIGURE 7: M-30
™
MODULATOR NON ANTILOCK EXHAUST OF SERVICE BRAKES (NORMAL)
BRAKE VALVE
SPRING
SUPPLY OR
HOLD
DIAPHRAGM
HOLD
VALVE
BIAS
VALVE
EXHAUST
DIAPHRAGM
EXHAUST
VALVE
BRAKE
CHAMBER
EXHAUST PORT


























