EN-92
Troubleshooting
EN-92
s
e
c
tio
n
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
3.
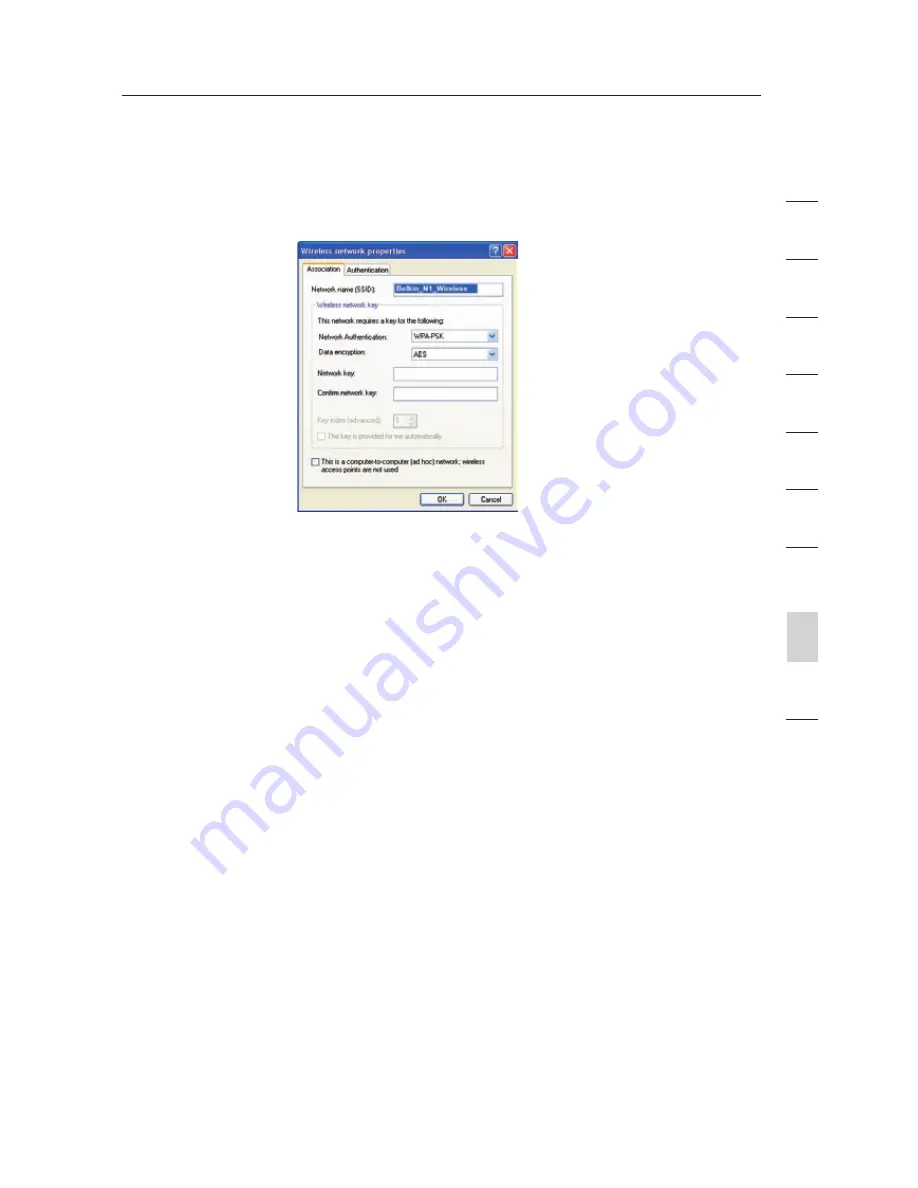
Under the “Wireless Networks” tab, click the “Configure” button
and you will see the following screen.
4.
For a home or small business user, select “WPA-PSK” under
“Network Administration”.
Note:
Select WPA (with radius server) if you are using this computer
to connect to a corporate network that supports an authentication
server such as a radius server. Please consult your network
administrator for further information.
5.
Select “TKIP” or “AES” under “Date Encryption”. This setting will
have to be identical to the Modem Router that you set up.
6.
Type in your encryption key in the “Network key” box.
Important:
Enter your pre-shared key. This can be from eight to 63
characters and can be letters, numbers, or symbols. This same key
must be used on all of the clients that you set up.
7.
Click “OK” to apply settings.
What’s the difference between 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11a, and
draft 802.11n?
Currently there are four levels of wireless networking standards, which
transmit data at very different maximum speeds. Each is based on
the designation for certifying network standards. The most common
wireless networking standard, 802.11b, transmits information at
11Mbps; 802.11a and 802.11g work at 54Mbps; and draft 802.11n
works at 108Mbps. See the chart on the next page for more detailed
information.









































