Mounting and wiring
BC5250
22
Version: 2.0.0
3.2.4
DeviceNet cabling
3.2.4.1
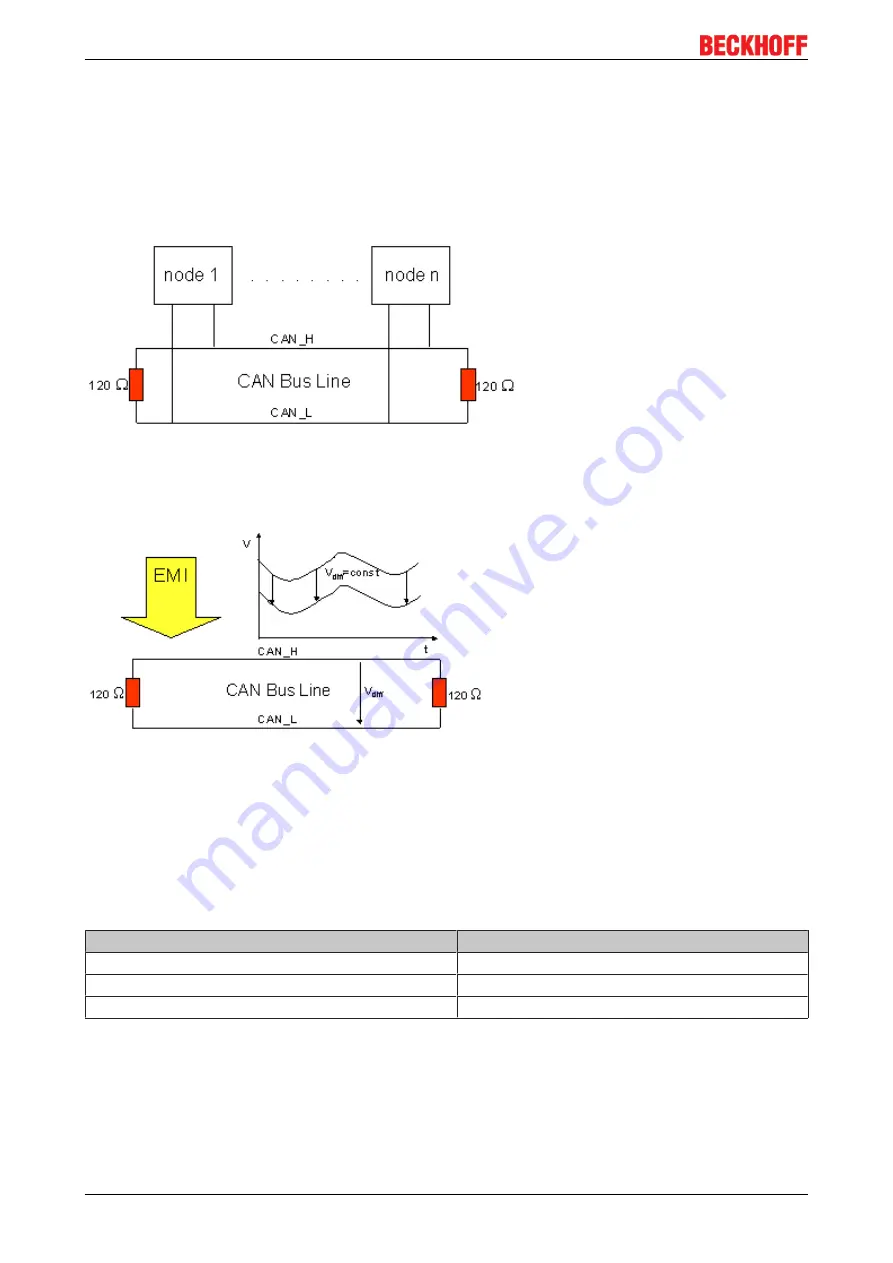
DeviceNet topology
CAN is a 2-wire bus system, to which all participating devices are connected in parallel (i.e. using short drop
lines). The bus must be terminated at each end with a 120 (or 121) Ohm termination resistor to prevent
reflections. This is also necessary even if the cable lengths are very short!
Fig. 11: Termination of the bus with a 120 Ohm termination resistor
Since the CAN signals are represented on the bus as the difference between the two levels, the CAN line is
comparatively not very sensitive to incoming interference (EMI). Both lines are affected, so the interference
has very little effect on the difference level.
Fig. 12: Insensitivity to incoming interference
3.2.4.2
Bus length
The maximum length of a CAN bus is primarily limited by the signal propagation delay. The multi-master bus
access procedure (arbitration) requires signals to reach all the nodes at effectively the same time (before the
sampling within a bit time). Since the signal propagation delays in the CAN connecting equipment
(transceivers, optocouplers, CAN controllers) are almost constant, the line length must be chosen in
accordance with the baud rate.
Baud rate
Bus length
500 kbit/s
< 100 m
250 kbit/s
< 250 m
125 kbit/s
< 500 m
3.2.4.3
Drop lines
Drop lines must always be avoided as far as possible, since they inevitably cause signal reflections. The
reflections caused by drop lines are not however usually critical, provided they have decayed fully before the
sampling time. In the case of the bit timing settings selected in the Bus Couplers it can be assumed that this
is the case, provided the following drop line lengths are not exceeded:
















































