Avaya G250 and G250-BRI Branch Office Media Gateways w/FIPS Non-Proprietary Security Policy
Version 1.2 Wednesday, 14 December, 2005
© 2005 Avaya Inc.
May be reproduced only in its original entirety [without revision]. Page 17 of 23
CID 106595
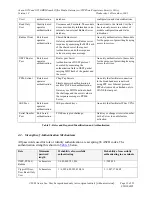
Key
Description/Usage
Radius Secret
Used for hashing password with MD5. One secret common to both
primary and Secondary Radius server.
OSPF Secret
Used for authentication OSPF messages with the Peer OSPF routers.
Secret exchanged hashed using MD5. One secret defined per peer
router identity.
PPPoE CHAP/PAP Secret
Used for authentication to PPPoE server.
SNMPv3 user authentication password
SNMPv3 operator MD5 authentication password used for
authenticating the User and Read-Only User roles.
Fixed Serial Number secret
The TDES key used for the serial number exchange protocol.
Ephemeral Serial Number secret
The TDES key used for the serial number exchange protocol.
X9.31 PRNG State
Internal state for X9.31 PRNG
Table 8 – CSPs and private keys
The following are the public keys contained in the module:
Key
Description/Usage
IKE Ephemeral DH Phase
–1 public keys
Generated for VPN IKE Phase 1 key establishment.
IKE Ephemeral DH Phase
–2 public keys
Generated for VPN IKE Phase 2 PFS key renewal.
Image download
certificate (Avaya root CA
RSA public key)
Used for authentication of software download. The Avaya Root certificate is hard-
code in Gateway image and used directely for authentication of the chain of trust of
the Avaya Signing Authority that is downloaded together with the software.
License download public
key
Used for authentication of license file validity. The license signing authority public
key is hard-code in Gateway image and used directely for authentication of the
digital signature embedded in the license file.
Table 9 – Public keys
5.4.
Definition of CSPs Modes of Access
Table 10
below defines the relationship between access to CSPs and the services. The modes of
access shown in the table include:
•
Read: the data item is read from memory.
•
Write: the data item is written into memory.
•
Zeroize: the data item is actively overwritten.