44
Glossary
CFU (colony-forming unit)
Unit by which the culturable number of microorganisms is expressed. [DIN EN 13098]
Disinfection
Method aiming to reduce the number of viable-microorganisms in a liquid or on a surface to such extent that
an infection hazard no longer exists.
Clean swept
Condition of a surface which was cleaned using, e. g., a broom or brush and which, under visual inspection,
can be termed clean.
Hygiene
Measures which serve to prevent diseases as well as to maintain and promote health.
Hygiene inspection
Qualified investigation of the hygienic condition of ventilation and air-conditioning systems.
Hygiene check
Periodic observation of the hygienic condition of ventilation and air-conditioning systems at short intervals.
Air hygiene
That branch of hygiene dealing with the interactions between man and the ambient breathing air which are
relevant to health and well-being.
Microorganisms
In the context of ventilating and air-conditioning systems, this term is taken to subsume bacteria (such as
legionellae), algae and moulds capable of multiplying in water or on humid surfaces (such as in the humidifier
water or in condensate).
Ventilating and air-conditioning systems and air handling units
The total of all components required for fan-driven ventilation of one or several rooms.
Evaporative Cooling
A process in which liquid water is evaporated into air. The liquid absorbs the heat necessary for the
evaporation process from the air, thus, there is a reduction in air temperature and an increase in the actual
water vapor content of the air.
Dry-bulb temperature (DBT)
Temperature of air measured by a thermometer freely exposed to the air but shielded from radiation and
moisture. DBT is the temperature that is usually thought of as air temperature.
Wet-bulb temperature (WBT)
The lowest temperature that can be reached under current ambient conditions by the evaporation of water
only; it is the temperature felt when the skin is wet and exposed to moving air.
Relative Humidity(RH)
The ratio of the vapor pressure (or mole fraction) of water vapor in the air to the vapor pressure
(or mole fraction) of saturated air at the same dry-bulb temperature and pressure.
Adiabatic or Evaporative Cooling (Humidification)
A thermodynamic or psychrometric process that involves the cooling of air without heat loss or gain.
Sensible heat lost by the air is converted to latent heat in the added water vapor (cools air temperature).
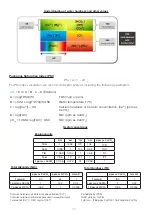
Saturation efficiency or cooling effectiveness
The Saturation Efficiency
(η)
or Cooling Efficiency is expressed in % and corresponds to the ratio between
the entering dry bulb temperature and exiting dry bulb temperature over the wet bulb depression.
Molar mass
In chemistry, it is defined as the mass of a given substance (chemical element or chemical compound)
divided by its amount of substance.[1] The base SI unit for molar mass is kg/mol. However, for historical
reasons, molar masses are almost always expressed in g/mol.
Water hardness
The simple definition of water hardness is the amount of dissolved calcium and magnesium in the water.
Содержание EvaPack Series
Страница 46: ...46 Notes...
Страница 47: ...47 Notes...