9 (54)
3.4
Communication Settings
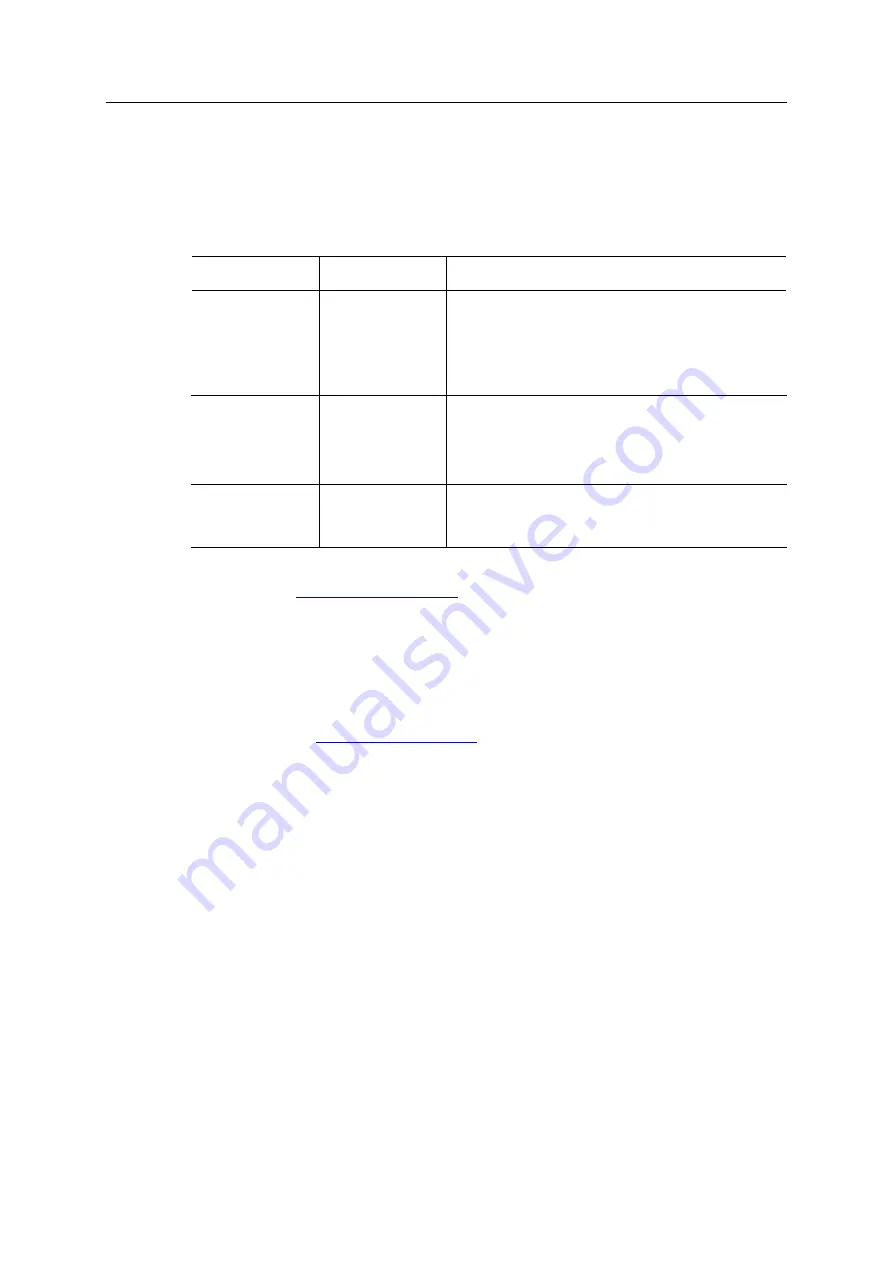
IP address communication settings are configured by the “Application switch 1” register. An
application may select to write the value from a physical DIP switch, rotary switch or similar, to
this register or it can assign it by other means.
“Application switch 2” is not used for EtherNet/IP network configuration.
Application switch 1
value
User communication
settings
Comment
0
Use currently stored
communication settings
Factory default stored communication settings:
IP address: 0.0.0.0
Subnet mask: 0.0.0.0
Gateway address: 0.0.0.0
DHCP: ON
Note
: Communication settings may be set by external software, see
below.
1-254
IP address: 192.168.0.X
Subnet mask:
255.255.255.0
Gateway address:
0.0.0.0
DHCP: OFF
Where X in the IP address is the “Application switch 1” value.
Resulting communication settings are stored and can later be used
if “Application switch 1” value is set to 0.
255
IP address: N/A
Subnet mask: N/A
Gateway address: N/A
DHCP: ON
Communication settings received by DHCP are stored and can later
be used if “Application switch 1” value is set to 0.
The communication settings can also be changed from the internal web page, using the IPConfig
tool, available at
, or through the EtherNet/IP network. Note that
changing the configuration through any of these interfaces will affect the currently used and/or
stored configuration, but will only be used after the next restart if “Application switch 1” is set to
0.
3.4.1
IPConfig
The IP address can also be configured using the IPConfig tool that is available for download at
the product page at
.
When the application is started, the network is automatically scanned for Anybus products. The
network can be rescanned at any time by clicking
Scan
.
To alter the network settings of a module, double-click on its entry in the list. A window will
appear, containing the settings for the module.
Validate the new settings by clicking
Set
, or click
Cancel
to cancel all changes.
3.5
Beacon Based DLR (Device Level Ring)
Device Level Ring (DLR) is a network technology for industrial applications that uses embedded
switch functionality in automation end devices, such as programmable automation controllers
and I/O modules, to enable Ethernet ring network topologies at the device level. DLR technology
adds network resilience to optimize machine operation. Beacon based DLR networks consist of a
ring supervisor and a number of ring nodes, and use “beacons” to detect breaks in the ring.
When a DLR network detects a break in the ring, it provides ways to alternatively route the data
to recover the network. Diagnostics built into DLR products can identify the point of failure, thus
helping to speed maintenance and reduce repair time. The Anybus CompactCom B40 Modbus
Serial - EtherNet/IP implements the DLR protocol, which is always enabled. The device is able to
process and act on beacon frames sent by ring supervisors, and supports beacon rates down to
100 μs.
Anybus
®
CompactCom
™
B40 Modbus Serial EtherNet/IP Network Guide
SCM-1202-131 1.1 en-US


























