UG-439
Evaluation Board User Guide
Rev. A | Page 4 of 13
Figure 2. BUCK1 External Output Voltage Setting
Setting the Output Voltage of the LDO Regulators
Each LDO output voltage is set through external resistor
dividers, as shown in Figure 3, for LDO1. The output voltage can
optionally be factory programmed to default values as indicated in
the
ADP5034
data sheet. In this event, FB3 must be connected to
the top of the capacitor on VOUT3 by placing a 0 Ω resistor on
R
TOP
, and leave R
BOT
unpopulated. Refer to Table 2 for the
corresponding 0 Ω resistor placements on R
TOP
per channel.
Figure 3. LDO1 External Output Voltage Setting
External Resistor Divider Setting for Buck and LDO
Regulators
The
ADP5034
TSSOP evaluation boards are supplied with fixed
resistor dividers with values chosen for a target output voltage.
Varying the resistor values of the resistor divider networks
varies the output voltage accordingly.
Table 2. External Resistor Dividers
Resistor Divider
Buck 1
Buck 2
LDO1
LDO2
R
TOP
RT1 RT2 RT3 RT4
R
BOT
RB1 RB2 RB3 RB4
MEASURING EVALUATION BOARD PERFORMANCE
Measuring Output Voltage Ripple of Buck Regulators
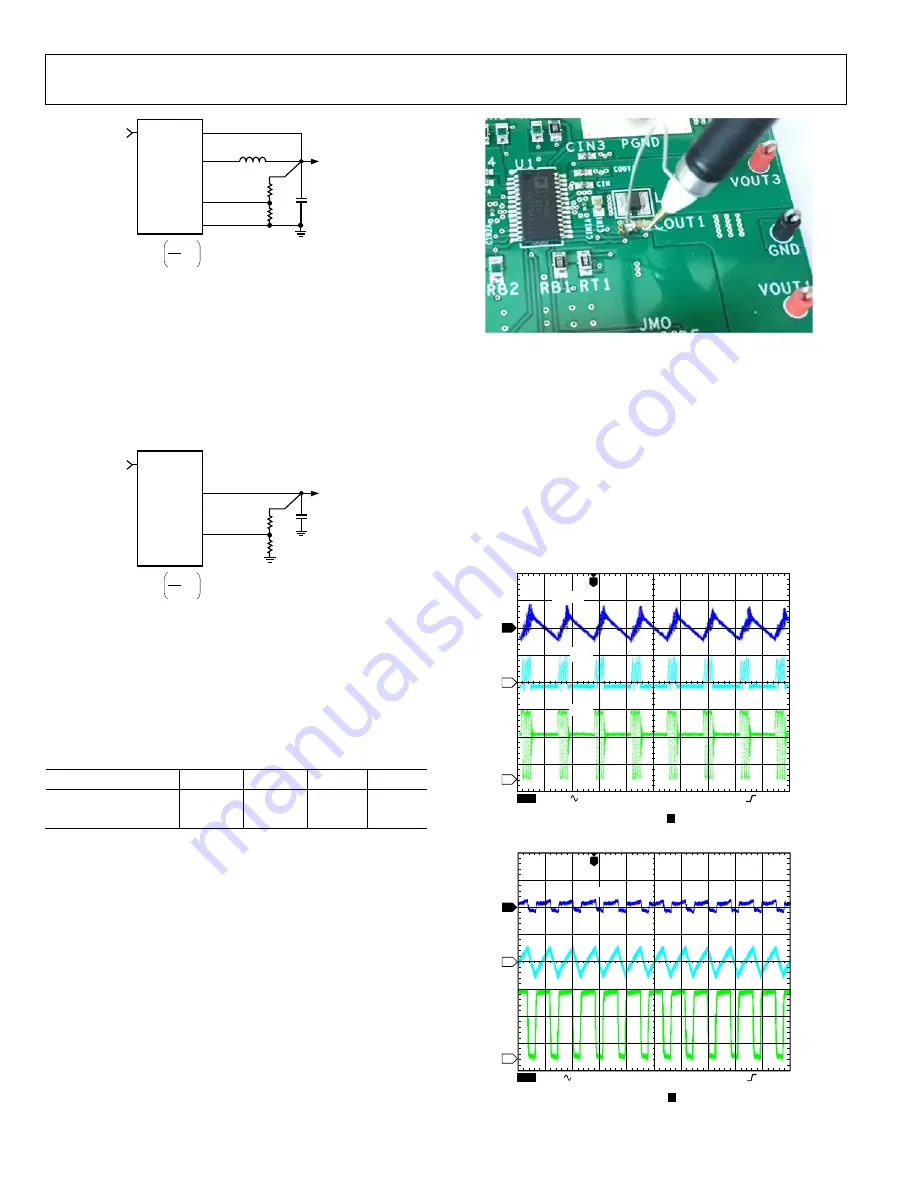
To observe the output voltage ripple of Buck 1, place an oscillo-
scope probe across the output capacitor (COUT1) with the probe
ground lead at the negative (−) capacitor terminal and the probe
tip at the positive (+) capacitor terminal.
Set the oscilloscope to ac, 10 mV/division, and 2 μs/division
time base, with the bandwidth set to 20 MHz to prevent noise
from interfering with the measurements. It is also recommended
to shorten the ground loop of the oscilloscope probe to minimize
coupling. One way of measuring the output voltage ripple is to
solder a wire to the negative (−) capacitor terminal and wrap it
around the barrel of the probe, while the tip directly connects to
the positive (+) capacitor terminal, as shown on Figure 4.
Figure 4. Measuring Output Voltage Ripple
Measuring the Switching Waveform of Buck Regulators
To observe the switching waveform with an oscilloscope, place
the oscilloscope probe tip at the end of the inductor with the probe
ground at GND. Set the oscilloscope to dc, 2 V/division, and
200 ns/division time base. When the MODE pin is set to high, the
buck regulators operate in forced PWM mode. When the MODE
pin is set to low and the load is above a predefined threshold, the
buck regulators operate in PWM mode. When the load current
falls below a predefined threshold, the regulator operates in PSM,
improving the light load efficiency. Typical PWM and PSM
switching waveforms are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
Figure 5. Typical Waveforms, V
OUT2
= 3.3 V, I
OUT2
= 30 mA, PSM Mode
Figure 6. Typical Waveforms, V
OUT2
= 3.3 V, I
OUT2
= 30 mA, PWM Mode
BUCK
AGND
FB1
SW1
R1
R2
VOUT1
VOUT1
VIN1
L1
1µH
C5
10µF
V
OUT1
= V
FB1
+ 1
R1
R2
10895-
002
LDO1
FB3
R
TOP
R
BOT
VOUT3
VOUT3
VIN3
C7
1µF
V
OUT1
= V
FB3
+ 1
R1
R2
1089
5-
003
1
0895-
0
04
2
4
T
1
CH1
50.0mV
M 4.00µs A CH2 240mA
T
28.40%
CH2 500mA
Ω
CH4 2.00V
I
SW
VOUT2
SW2
1
0895-
0
05
2
4
T
1
CH1
50mV
M 400ns
A CH2 220mA
T
28.40%
BW
CH2 500mA
Ω
CH4 2.00V
BW
I
SW
VOUT2
SW2
108
95-
006






























