41-133S
8
Directional Overcurrent Ground Relays
Types IRP, IRC and IRD
b.
The contact gap adjustment for the overcurrent
unit is made with the moving contact in the reset
position i.e., against the right side of the bridge.
Move in the left-hand stationary contact until it
just touches the moving contact then back off the
stationary contact 2/3 of one turn for a gap of
approximately .020”. The clamp holding the sta-
tionary contact housing need not be loosened for
the adjustment since the clamp utilizes a
spring-type action in holding the stationary con-
tact in position.
c.
The sensitivity adjustment is made by varying
the tension of the spiral spring attached to the
moving element assembly. The spring is
adjusted by placing a screwdriver or similar tool
into one of the notches located on the periphery
of the of the spring adjuster and rotating it. The
spring adjuster is located on the underside of the
bridge and is held in place by a spring type
clamp that does not have to be loosened prior to
making the necessary adjustments.
Before applying current, block open the nor-
mally-closed contact of the directional unit insert
the tap screw in the minimum value tap setting
and adjust the spring such that the contacts will
close as indicated by a neon lamp in the contact
circuit when energized with the required current.
The pick up of the overcurrent unit with the tap
screw in any other tap should be within 5% of tap
value.
If adjustment of pick-up current in-between tap
settings is desired insert the tap screw in the next
lowest tap setting and adjust the spring as
described. It should be noted that this adjustment
results in a slightly different time characteristic
curve and burden.
7.4.1 Directional Unit (D)
In the type IRP and IRC relays the directional unit is
the lower cylinder unit. In the type IRD the directional
units are the lower and middle cylinder units.
a.
The upper bearing screw should be screwed
down until there is approximately .025 clearance
between it and the top of the shaft bearing. The
upper pin bearing should then be securely
locked in position with the lock nut.
b.
Contact gap adjustment for the directional unit is
made with the moving contact in the reset posi-
tion, i.e., against the right side of the bridge.
Advance the right hand stationary contact until
the contacts just close. Then advance the sta-
tionary contact an additional one-half turn.
Now move in the left-hand stationary contact
until it just touches the moving contact. Then
back off the stationary contact 3/4 of one turn for
a contact gap of .020” to .024”. The clamp hold-
ing the stationary contact housing need not be
loosened for the adjustment since the clamp uti-
lizes a spring-type action in holding the station-
ary contact in position.
c.
Insert tap screw of overcurrent unit in highest
tap. The sensitivity adjustment is made by vary-
ing the tension of the spiral attached to the mov-
ing element assembly. The spring is adjusted by
placing a screwdriver or similar tool into one of
the notches located on the periphery of the
spring adjuster and rotating it. The spring
adjuster is located on the underside of the bridge
and is held in place by a spring type clamp that
does not have to be loosened prior to making the
necessary adjustments. Set red mark on core to
left side of cylinder unit and adjust spring to just
reset.
The spring is to be adjusted such that the con-
tacts will close as indicated by a neon lamp in the
contact circuit when energized with the required
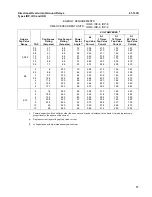
current and voltage as shown in Table 1 (page
10). This table indicates that the spring can be
adjusted when the phase angle relationship
between the operating circuit and the polarizing
circuit is at the maximum torque angle or when
the circuit relationship has the operating and
polarizing circuits in phase.
d.
The magnetic plugs are used to reverse any
unwanted spurious torques that may be present
when the relay is energized on current or voltage
alone.
The reversing of the spurious torques is accom-
plished by using the adjusting plugs in the follow-
ing manner:
1.
Voltage circuit terminals on the voltage
polarized relays (IRP and IRD voltage polar-
ized unit) are short-circuited.
2.
The polarizing circuits of the current polar-
ized relays (IRC and IRD current polarized
unit) are open-circuited.