User manual
28
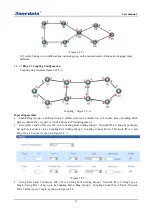
Rapid Spanning Tree of concepts:
Switch priority
:
As the bridge priority
,
the bridge priority and bridge MAC address combine bridge ID
,
the smallest ID bridge will become the root bridge on the network.
Polling interval
:
how often send BPDU packet at one time.
Forwarding delay
:
the port state of switch remain a forward delay time over the listening and learning.
The maximum aging time
:
After one switch receive a packet from other switches , how long the packet is
valid
The port concepts of RSTP:
Port path overhead
:
port link cost compared with port priority and port ID .
Port priority
:
port priority among the net bridge compared with port priority and port ID.
Point to point network connection
:
directly connect with switches port each other ,the port is P2P,which
adopted negotiation mechanism,RSTP can achieve port state rapid conversion RSTP.
Directly connect terminal
:
connect the edge of network switch with terminal devices with
configuration
Edge port
,
which can achieve port state rapid conversion without the processing Discarding
,
Learning
,
Forwarding.
Don’t join RST structure
:
don‘t participate in RSTP running.
RSTP switch port states:
1.
Blocking
- A port that would cause a switching loop if it were active. No user data is sent or received over
a blocking port, but it may go into forwarding mode if the other links in use fail and the spanning tree
algorithm determines the port may transition to the forwarding state. BPDU data is still received in blocking
state. Prevents the use of looped paths.
2.
Listening
- The switch processes BPDUs and awaits possible new information that would cause it to
return to the blocking state. It does not populate the MAC address table and it does not forward frames.
3.
Learning
- While the port does not yet forward frames it does learn source addresses from frames
received and adds them to the filtering database (switching database). It populates the MAC Address table,
but does not forward frames.