ZXR10 ZSR V2 Configuration Guide (IPv6)
1111111010
0
Interface identifier
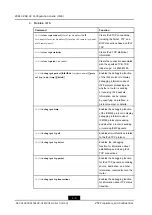
Site-local Address
10
38
16
64
1111111011
0
Subnet
identifier
Interface identifier
Link-local addresses are used in a single network link for host numbering. The address
identified by the first ten bits of the prefix is the link-local address. Routers do not
process the packets with link-local addresses at their source end and destination end
because they never forward these packets.
The middle 54 bits of this address are set to zero, its 64-bit interface identifier is in the
same IEEE structure as mentioned in the foregoing paragraphs, and the part of this
address space allows some networks to connect up to 2
64
-1 hosts.
Link-local addresses are used for the single network link and site-local addresses are
used for sites. It means that site-local addresses can be used to transmit data in the
interconnected networks but cannot be directly routed to the global Internet from a
site.
Routers within a site can only forward packets within the site instead of forwarding
them outside of the site. The 10-bit prefix of a site-local address is immediately
followed by a succession of zeros, which is slightly different from that of a link-local
address. The subnet identifier of a site-local address is 16-bit, and its interface
identifier is still the 64-bit IEEE-based address.
Note that the special behavior of site-local addresses has been removed from RFC.
Addresses such as fec0::/10 need to be treated as common unicast addresses.
l
Open Systems Interconnection (
) Network Service Access Point (
) Address
and Internetwork Packet Exchange (
) Address
One of the IPv6 objectives is to unify the whole network world for among IP, IPX, and
OSI networks. To support this interoperatability, IPv6 reserves 1/128 address space
for OSI NSAP address and network IPX address respectively.
At present, the IPX addresses have not been precisely defined. Refer to RFC for
description of the NSAP address allocation.
Multicast Address
The format of the IPv6 multicast address is different from that of the IPv6 unicast address.
Multicast addresses can only be used as destination addresses.
No packet uses a
multicast address as the source address.
lists the format of a multicast address.
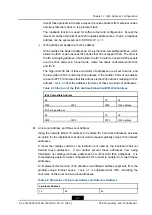
Table 2-5 Multicast Address Format
8
4
4
112
1111111
Flags
Scope
Group identifier
2-8
SJ-20140504150128-018|2014-05-10 (R1.0)
ZTE Proprietary and Confidential