User Manual
P a g e
| 68
B:
The following uses four examples to describe the preceding principles.
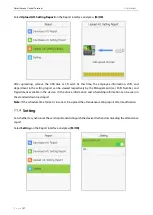
Example 1: Normal attendance
Attendance Time Range
09:00 — 12:00
13:00 — 18:00
Attendance time of #1
employee
8:30, 8:35, 11:55,12:01, 12:50, 18:02,19:00
Statistical result based on
attendance rules
8:30
12:01
12:50
18:02
Description:
The attendance time 8:30 and 8:35 are earlier than the on-duty time 9:00 and they are within
the normal attendance time range. Therefore, 8:30 is adopted for the on-duty time 9:00 based on the
principle of adopting the earliest time for normal attendance. 18:02 and 19:00 are later than the off-duty
time 18:00, and therefore, 18:02 is adopted based on the same principle.
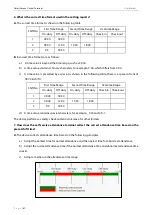
Example 2: Late arrival
Attendance Time Range
09:00 — 12:00
13:00 — 18:00
Attendance time of #1
employee
9:01, 9:04, 12:01, 12:50, 18:00
Statistical result based on
attendance rules
9:01
12:01
12:50
18:00
Description:
Employer 1 checks in for work at 9:01 and 9:04 and he/she is late based on the preset on-duty
time. Based on the principle of adopting the nearest time for abnormal attendance, the correct check-in
time is 9:01 rather than 9:04 because of 9:01 is nearer 9:00.
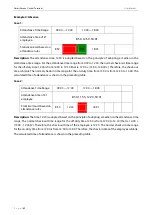
Example 3: Early leave
Attendance Time Range
09:00 — 12:00
13:00 — 18:00
Attendance time of #1
employee
8:50, 11:40,11:55, 12:50, 18:01
Statistical result based on
attendance rules
8:50
11:55
12:50
18:01
Description:
The attendance time 12:50 is adopted based on the principle of adopting a median in the
attendance time range. For the attendance time range from 9:00 to 12:00, the normal check-out time range
for the off-duty time 12:00 is from 12:00 to 12:30 (that is, 12:00 + (13:00 - 12:00)/2). Therefore, the calculated
time of attendance is shown in the preceding table.
Smart Access Control Terminal