-23-
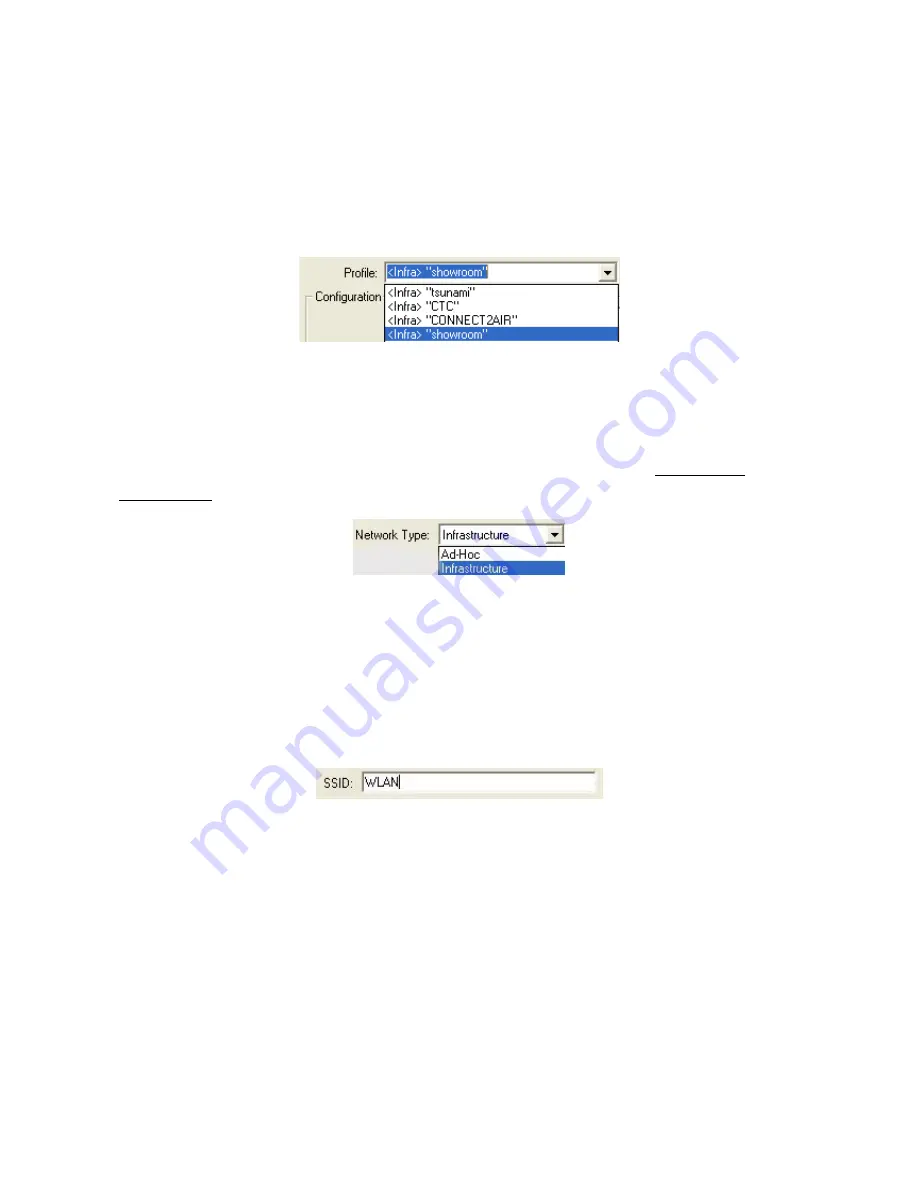
Profile
The
Profile
field allows you to set values for all parameters by selecting a previously defined
profile. To create the profile, go to the
Profile
field, type a profile name and set the corresponding
parameters. If one of the profiles is no longer used, you may remove it by clicking the
Delete
button.
After changing parameters, save the profile and click the
Apply
button to take effect. You can have
multiple profiles and modify the profile at any time.
Network Type
There are two network types for the IEEE 802.11g Wireless LAN USB Adapter to operate. If you
need to access company network or Internet via an Access Point, select “
Infrastructure
”. To set up
a group of wireless stations for file and printer sharing, select “
Ad-Hoc
” (without Access Point).
For standard
802.11 Ad-Hoc
,
note that you may set wireless stations with the
same ESS ID
and the
same channel
.
SSID
The SS ID is the unique ID used by Access Points and stations to identify a wireless LAN. Wireless
clients associating to any Access Point must have the same SSID. The default setting is ANY,
which allows your IEEE 802.11g Wireless LAN USB Adapter to automatically associate to any
Access Point (Infrastructure mode) in the vicinity of your wireless adapter. The ESS ID can be set
up to
32 characters
and is case sensitive.
Transmit Rate
The IEEE 802.11g Wireless LAN USB Adapter provides various data rate options for you to select.
Data rates options include
Fully Auto
,
1 or 2 Mb
,
5.5 Mb
,
11 Mb and up to 54Mb
in most
networking scenarios, you will see that the factory-set default “
Auto
” will prove the most efficient.
This setting will allow your IEEE 802.11g Wireless LAN USB Adapter to operate at the maximum
data rate. When the communications quality drops below a certain level, the Wireless LAN USB
Adapter will automatically switch to a lower data rate. Transmission at lower data speed is usually
more reliable. However, when the communications quality improves again, the Wireless LAN USB
Adapter will gradually increase the data rate again, until it has reached the highest available
transmit rate.




























