EAD10 Reference Manual (Advanced)
47
File
A knowledge of terms is required to understand the functions and operations of the MENU/File section. This section
explains the terminology used in the MENU/File section.
File
The term “file” is used to define a set of data saved on a USB flash drive. Data exchanged between the EAD10 and a USB flash drive is
carried out in the form of files.
File Name
The name given to the file is called a file name. Files names are important for distinguishing files, and the same file name cannot be used
in the same directory. While computers can handle long names, and even include non-English characters, the EAD10 can only use alpha-
numeric characters.
Extensions
The “ three letters,” such as “.wav” at the end of the file name, is referred to as a “file extension.” The extension indicates the type
of file. Files that the EAD10 use have a “.bin” extension, which is not displayed on the EAD10 Screen.
File size
This refers to the size of the file. The file size is determined by the amount of data saved in the file. File size is measured in units indicated
with a B (byte). Large files and also the memory capacity of devices are represented using units of KB (kilobytes), MB (megabytes), and
GB (gigabytes). 1 KB=1024 B, 1 MB=1024 KB, and 1 GB=1024 MB.
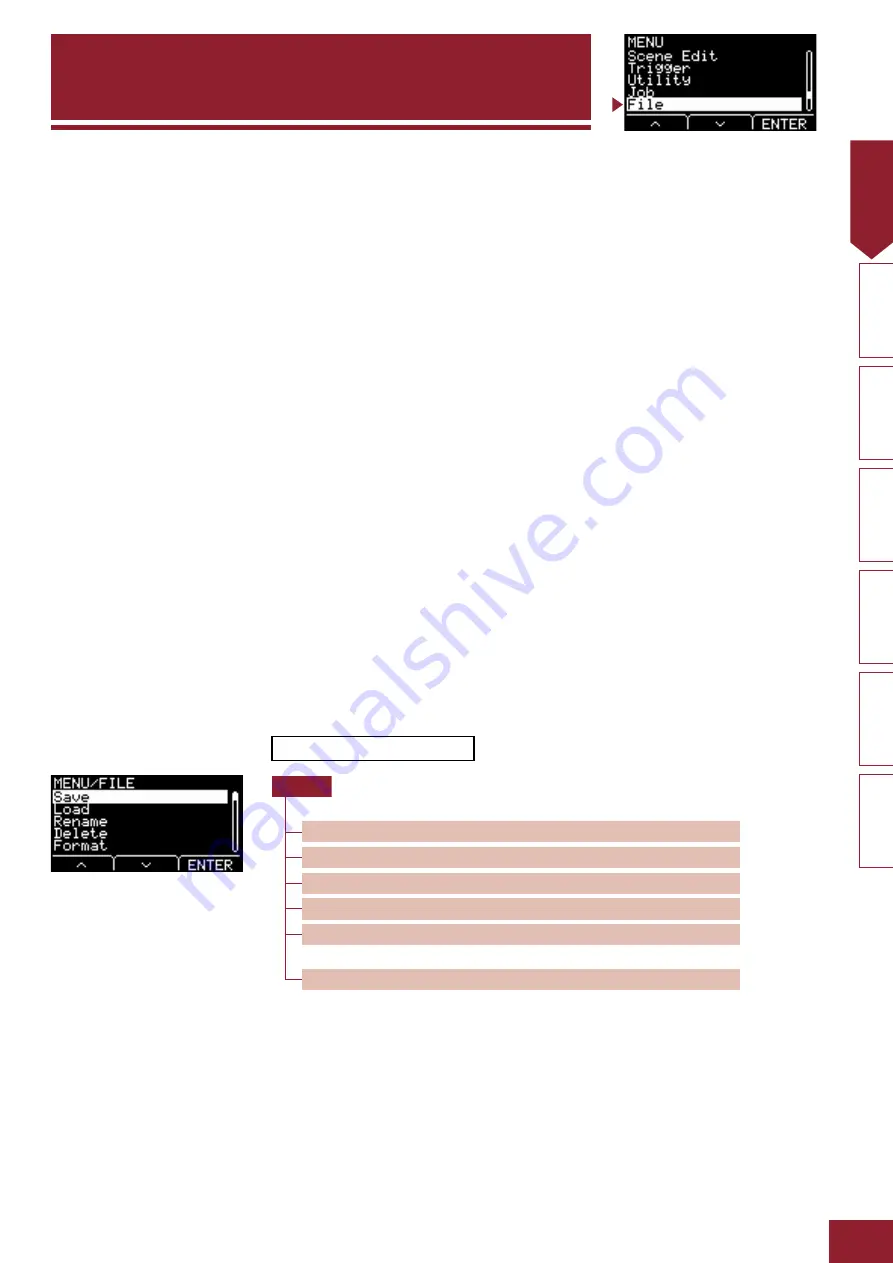
Format
Initializing the USB flash drive is known as “formatting.” Formatting a USB flash drive using the EAD10 will erase all files and directories
(or folders).
Save, Load
“Save” refers to the writing of data to a USB flash drive, while “load” refers to the reading of files from a USB flash drive.
The EAD10 can handle a maximum of 100 “.wav” files, and 100 “.bin” files.
For more information on cursor operations, refer to
NOTE
Settings Screen Structure
1/2
2/2
USB Flash Drive Memory Information
NOTE
File