11
P/N 10001646 Rev. AA
June 2015
MAINTENANCE
INSPECTION
To maintain continuous and satisfactory operation, a regular
inspection procedure must be initiated so that worn or damaged
parts can be replaced before they become unsafe. The intervals of
inspection must be determined by the individual application and are
based upon the type of service to which the hoist will be subjected.
The inspection of hoists is divided into two general classifications
designated as “frequent” and “periodic.”
Frequent Inspections:
These inspections are visual examinations by the operator or other
designated personnel. The frequent inspections are to be performed
daily and shall include the following items (no records required):
a. Braking mechanisms for evidence of slippage daily.
b. Load Chain for lubricant, wear, damaged links or foreign
material-daily (See pages 11, 12 & to 15).
c. Cracks or damage to housing, abnormal noises or operation,
damaged hooks (see Hook Inspection below).
d. All capacity and warning labels legible and present.
Any deficiencies noted are to be corrected before the hoist
is returned to service.
Periodic Inspections:
These are inspections by an appointed person who makes records
of apparent external conditions to provide the basis for a continuing
evaluation. For normal service, the periodic inspections are to be
performed yearly and for heavy service, the periodic inspections
are to be performed semi-annually.
Due to the construction of the hoist, it will be necessary to partially
disassemble the unit to perform the periodic inspections. The
periodic inspections are to include those items listed under frequent
inspections as well as the following:
a. Chain for excessive wear or stretch (See pages 11 to 12).
b. Worn, cracked or distorted parts such as hook blocks, hand
chain guides, chain guide, stripper, loose end connector, shafts,
gears, bushings and bearings.
c. Inspect for wear on the tip of the driver, stops on handwheel
and pockets of the liftwheel and handwheel.
d. Loose or missing screws, nuts, pins or cotter pins.
e. Inspect brake components for worn, glazed or contaminated
brake disc and scoring of the brake hub and brake plate. If the
thickness of the friction washer is less than 1/32 inch, it should
be replaced.
f. Replace missing or damaged warning labels.
g. Corroded, stretched or broken brake spring.
h. Hooks-dye penetrant, magnetic particle or other suitable crack-
detecting inspections should be performed at least once a year,
if external conditions indicate there has been unusual usage.
Any deficiencies noted are to be corrected before the hoist is
returned to service. Also, the external conditions may show the need
for more detailed inspection which, in turn, may require the use of
nondestructive-type testing.
Any parts that are deemed unserviceable are to be replaced with new
Columbus McKinnon parts before the unit is returned to service. It is
very important that the unserviceable parts be destroyed to prevent
possible future use as a repair item and properly disposed of.
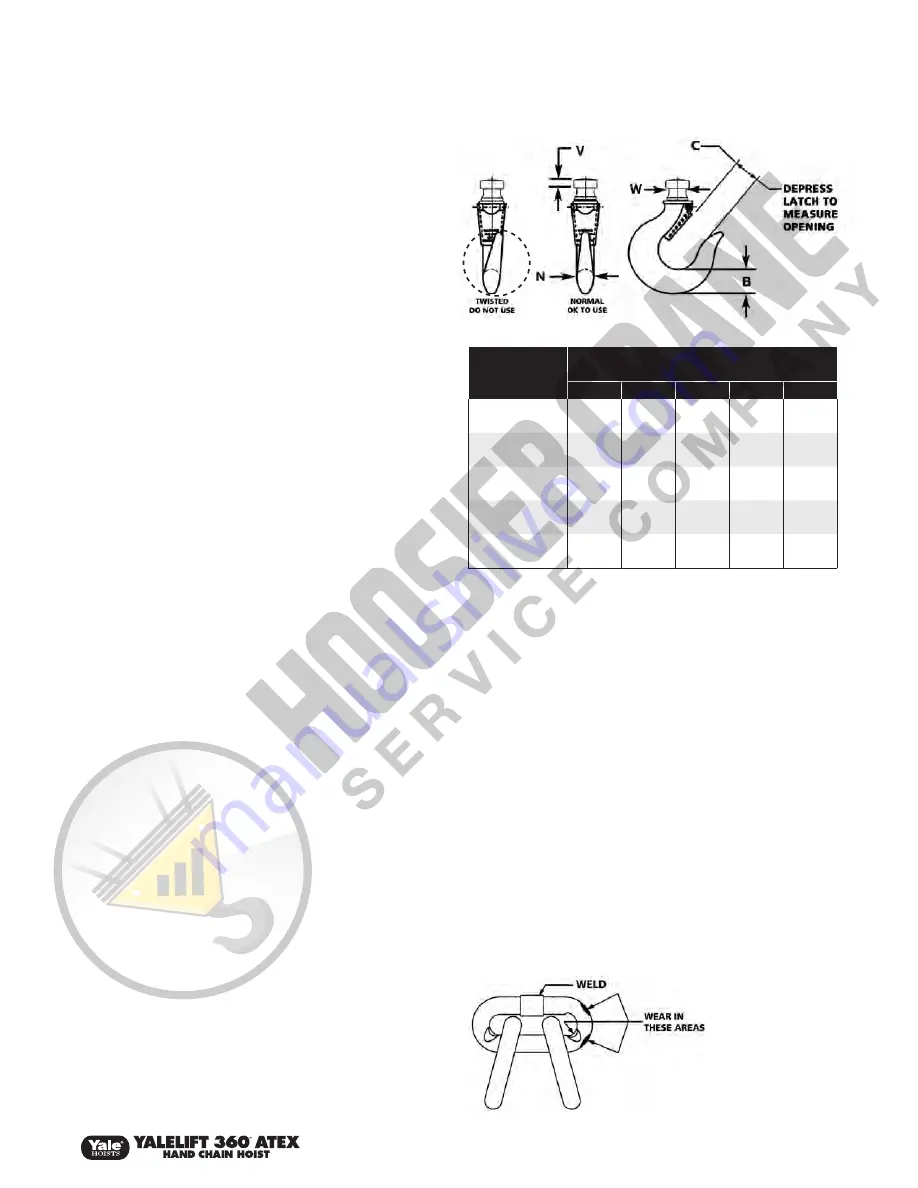
Hook Inspection
Hooks damaged from chemicals, deformation or cracks, or that have
a twist, excessive opening or seat wear, must be replaced. Also,
hooks that are opened to the extent that the latch does not engage
the tip must be replaced. Any hook that is twisted or has excessive
throat opening indicated abuse or overloading of the hoist. Other
load sustaining parts should be inspected for damage.
Check to assure the latch is not damaged or bent and that it operates
properly. It should have sufficient spring pressure to keep it tightly
against the tip of the hook and allow it to spring back to the tip when
released. If the latch does not operate properly, replace the latch.
LOAD CHAIN
Chain should feed smoothly into and away from the hoist. If chain
binds, jumps or is noisy, first clean and lubricate it (See next page). If
trouble persists, inspect chain and mating parts for wear, distortion
or other damage.
Chain Inspection
First clean chain with a non-caustic/non-acid type solvent and make
a link by link inspection for nicks, gouges, twisted links, weld spatter,
corrosion pits, striations (minute parallel lines), cracks in weld areas,
wear and stretching. Chain with any one of these defects must be
replaced.
Slack the portion of the chain that normally passes over the
liftwheel. Examine the interlink area for the point of maximum wear
(polishing). Measure and record the stock diameter at this point of
the link. Then measure stock diameter in the same area on the link
that does not pass over the liftwheel (use the link adjacent to the
loose end connector
for this purpose).
Compare these two
measurements. If the
stock diameter of the
worn link is 0.010 inch,
or more, less than the
stock diameter of the
unworn link, the chain
must be replaced.
TROLLEY
(YLITP/YLITG MODELS)
Check to make sure the side plates are parallel to each other.
Also, all wheels must be in contact with the beam flange.
ATTENTION: The trolley must never be used on beams with flange
widths that exceed the maximum adjustable width of the trolley.
Check the travel path before starting work to allow for unit to run
faultless on the beam. Any existing obstacles must be removed.
In addition, check the correct fastening and position of the end stops.
Figure 3 – Hook Inspection
Figure 4 - Chain Inspection
Capacity
(ton)
Critical Hook Dimensions
in.
(mm)
B
C
N
V
W
¼, ½ & 1
0.87
1.14
0.75
0.24
0.59
(22)
(29)
(19)
(6)
(15)
1½ & 2
1.50
1.58
1.18
0.43
0.87
(38)
(40)
(30)
(11)
(22)
3 & 4
1.77
1.85
1.46
0.47
1.10
(45)
(47)
(37)
(12)
(28)
5 & 6
2.68
2.68
1.97
0.67
1.38
(68)
(68)
(50)
(17)
(35)
8, 10 & 12
3.35
2.52
2.21
0.51
1.77
(85)
(64)
(56)
(13)
(45)
Hooks shall swivel freely under no load conditions. If there is any
binding, the hooks must be replaced. Also, replace hook if opening
is greater than “C” or if the thickness at “B”, “N”, “W”, or “V” is less
than the dimensions listed in the chart (see Figure 3).