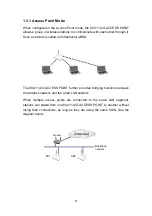
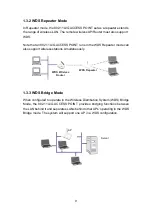
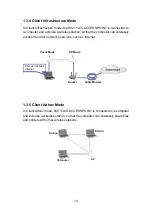
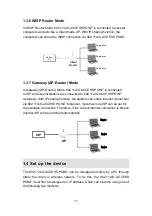
15
POINT, the PC client may not be able to reach the ACCESS POINT.
This is because they may no longer belong to the same IP network
address space.
Step 3.
Change the setting of the PC back to “obtain IP addresses
dynamically”.
Now you can put the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT and the PC to your
network where the DHCP server is connected. From then on, any
wireless client configured to “obtain IP addresses dynamically” will
work with the AP, with each other, and with devices on the wired LAN
network.
2.4 Set up a wireless client as a DHCP client
The following will give detailed steps of how to configure a PC or a wireless
client to “obtain IP addresses automatically”.
In the case of using a LAN attached PC, the PC must have an Ethernet
interface installed properly, be connected to the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT
either directly or through an external LAN switch, and have TCP/IP installed
and configured to obtain an IP address automatically from a DHCP server in
the network.
In the case of using a wireless client, the client must also have an 802.11a/b/g
wireless interface installed properly, be physically within the radio range of the
802.11A/G ACCESS POINT, and have TCP/IP installed and configured to
obtain an IP address automatically from a DHCP server in the network.
Then perform the following steps for either of the cases above. To configure
types of workstations other than Windows 95/98/NT/2000, please consult the
manufacturer’s documentation.
Step 1.
From
the
Win95/98/2000
Start Button, select Settings, then Control
Panel. The Win95/98/2000 Control Panel displays.
Step 2.
Double-click on the
Network
icon.
Step 3.
Check your list of Network Components in the Network window
Configuration tab. If TCP/IP has already been installed, go to Step 8.