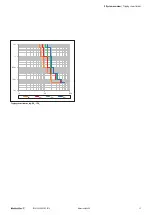
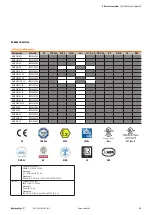
24
Manual maxGUARD
2526740000/02/03.2018
4 Configuration
| Connection to the control unit
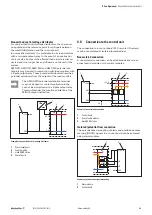
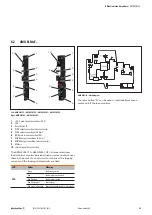
Non-earthed control voltage distributor
For non-earthed control voltage distributors, the shared mi-
nus potential is the reference point for all signals between
the maxGUARD station and the control board.
In non-earthed systems, it is preferable to use load monitors
with a two-pole output relay. In the event of an overload or
short circuit, all poles of the affected load circuit are discon-
nected and it no longer has any influence on the rest of the
system.
AMG PD, AMG OD, AMG MD and AMG DIS potential dis
-
tributors may be used in conjunction with load monitors with
a 2-pole output relay. These potential distributors draw their
potential exclusively from the outputs of the load monitors.
The AMG XMD potential distribution terminal
may not be used for contact replication in the
case of load monitors with a 2-pole output relay.
This would render the functional isolation at the
MINUS output ineffective.
+24 V
GND
1
2
3
4
+24 V
0 V
Example of a non-earthed control voltage distributor
1
Power supply unit
2
Feed-in module
3
maxGUARD station
4
Control board
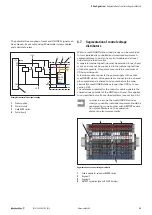
4.6 Connection to the control unit
The connection to a control board (PLC, remote I/O system)
may be non-isolated or isolated (potential-free).
Non-isolated connection
A non-isolated connection can be established either via an
active feed-in module or via control modules.
+24 V
GND
OUT
IN
2
3
1
+24 V
0 V
Reset
Alarm
Example of a non-isolated connection
1
Control board
2
Active feed-in module
3
maxGUARD station
Isolated (potential-free) connection
The potential-free decoupling of alarm and overload advance
warning (I>90%) signals to a control board can be achieved
using alarm modules.
2
Alarm
I>90%
1
+24 V
GND
IN
IN
Example of potential-free signal decoupling
1
Alarm module
2
Control board