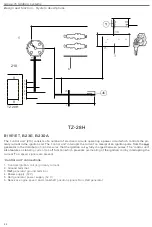
Group
28
fgnition
systems
Design
and function - System
descriptions
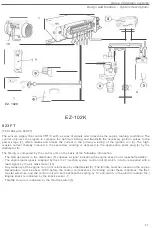
EZ-115K
EZ-115K
B280EIF
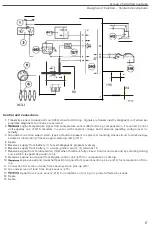
The
co
ntrol unit
(1) computes the optimum timing on
the
basis of information
from the
various sensors
and delivers
an ignition pulse at exactly the
cor
rect
ins
tant to the
power stage
which responds by making and breaking the
current
in the
primary winding of the ignition coil
(25).
The high-tension
cu
rrent
induced
in the
secondary winding by
interruption of the primary current is
fed
to
th
e
distribut
or (28)
for
delivery
to
the appropriate spark plug (29).
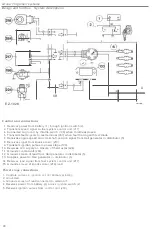
The
con
trol
unit computes the timing on
the
basis of the following information:
-
Engine
speed
and
crankshaft position signals are supplied by the speed
/
positi
o
n
pick-up
(2)
.
-
Engine
knock
detected by the
knock
sensors
(7)
.
-
Ignition in NO
.
1
cylinder is indicated by the No.1 cylinder detector (15)
.
-
Engine
load signals are
supplied
by
the
fuel injection system
control
unit (19).
-
Eng
i
ne
temperature
is
indicated by
th
e
t
empera
ture
sensor
(23)
.
-
Closure of the
throttle
is
ind
icated by
the throttle
switch
(2
4
)
.
The
ignition
pulse
is interrupted by
the contro
l
unit
at a speed of
approx. 6300
r/min.
Th
e
control unit
can
vary the timing from
approx.
60
°
before TDC to approx. "
.
after
TD
C.
55