UNAOHM
16
NG500 (Rev. 0)
8.
APPENDIX – THERMAL NOISE
All electronic components, both passive and active, generate a signal caused by the thermal
agitation of the electrons that are freed from their respective atoms and move without restraint in
the conductor.
The free electrons are in constant and chaotic motion among the practically still atoms in the
metal. Their motion, as that of the molecules of a liquid, increases considerably in speed as the
temperature of the conductor increases and is an electric indication of the temperature itself.
As a result of the thermal motion of the freed electrons, a conductor may be retained neutral only
from a global and average point of view, while the number of electrons in each part of it changes
from one moment to another.
In particular, across a resistor there is never at any given moment the same number electrons
and therefore a difference in potential.
Since the situation undergoes constant change due to the chaotic motion of the electrons, the
difference in potential varies continuously in a totally irregular manner while, in any case,
remaining at an average of zero.
We are therefore dealing with zero average voltage with momentary values that are extremely
low that may be noted only if highly amplified. This does not, however, signify that it is less
real than the normal voltages obtained by the generators.
Thermal noise spectral distribution is the simplest possible since its spectral density has a
constant value
φ
, from the lowest to the highest frequencies.
Theoretical considerations, backed up by specific experimental comparisons, confirm that
φ
is
proportional to the “R” resistance and to the absolute temperature “T”, according to the
relationship
φ
= 4KTR.
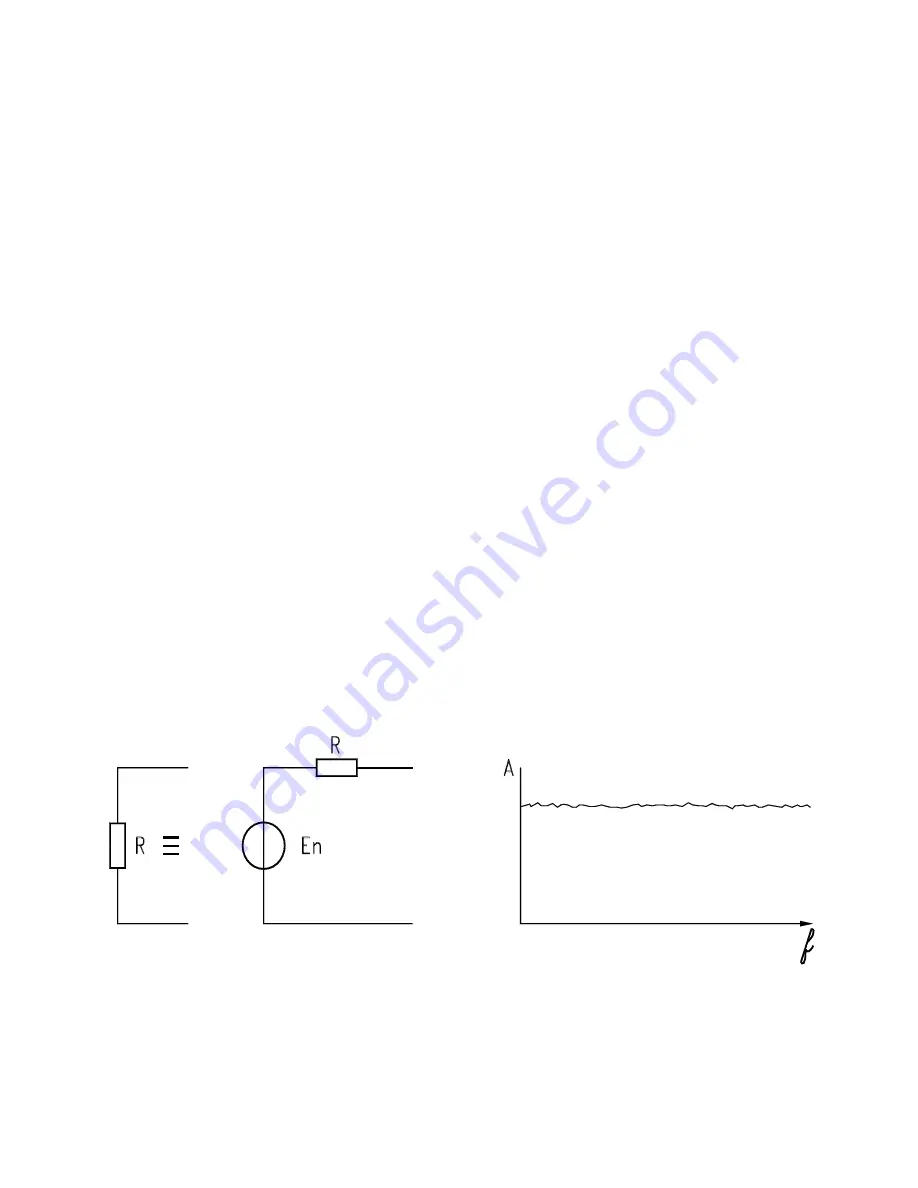
The simplest case to be referred to is that of a conductor with resistance “R” whose thermal
noise, due to the free electrons’ agitation, creates an instantaneous voltage Vn across itself..
Figura 7 Equivalent circuit of a noise generator
The equivalent circuit is shown in Figure 7 having ideally taken into consideration a noise
generator Vn (generated precisely by the resistance “R”) and by a series resistance free of noise).




































