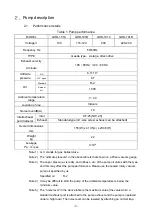
-7-
3.3 Vacuum
piping
(1) Remove any powder, dust, or rust from the internal walls of the vacuum chamber,
piping, and vacuum valve etc. before connection to the pump.
The metal mesh in the inlrt port prevents introduction of foreign matter into the pump.
Do not remove it during use. Introduction of powder and dust into the pump will result
in a malfunction. If moisture is introduced to the pump, not only will the ultimate
pressure increase, but the inside of the pump will rust and may lead to the pump
malfunctioning.
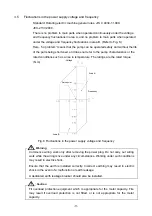
(2) Install the vacuum valve (A) and leak valve (B) between the vacuum chamber and
pump as shown in Fig. 4.
Fig. 4 Vacuum chamber and basic piping connections
(3) This pump is fitted with an oil backflow prevention device. It is effective for preventing
the oil from back flowing when the pump is stopped. (It is not a gas backflow
prevention device.)
The backflow prevention device uses the oil pressure inside the pump to return the
internal pressure to atmospheric pressure when the pump is stopped and to close
the valve directly below the intake.
The backflow prevention device does not guarantee to do this 100%. In the case that the
internal pressure is not returned to atmospheric pressure when the pump is stopped,
approximately 400 ml of oil will enter the vacuum chamber in a short time. Also, even if
the internal pressure is returned to atmospheric pressure when the pump is stopped, the
pressure in the vacuum chamber will return to atmospheric pressure in a short time.
In addition to installing the vacuum valve (A) and leak valve (B) between the vacuum
chamber and pump as shown in Fig. 4., ensure that there is more capacity between the
pump and vacuum chamber that the amount of the oil backflow.
Vacuum
(A)
Vacuum valve
Leak valve
(B)
Pump
Attention
Warning