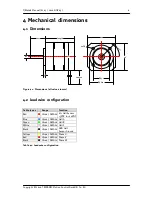
QBL4208 Manual (V1.03 / 2010-NOV-03)
12
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
6
Motor sizing
For the optimum solution it is important to fit the motor to the application. The three key parameters
are peak torque requirement, RMS torque requirement and motor velocity.
6.1
Peak torque requirement
Peak torque T
P
is the sum of the torque due to acceleration of inertia (T
I
), load (T
L
) and friction (T
F
):
F
L
J
P
T
T
T
T
The torque due to inertia is the product of the load (including motor rotor) inertia and the load
acceleration:
a
J
T
J
The torque due to the load is defined by the configuration of the mechanical system coupled to the
motor. The system also determines the amount of torque required to overcome the friction.
6.2
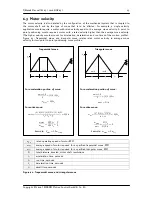
RMS torque requirement
Root-Mean-Square or RMS torque is a value used to approximate the average continuous torque
requirement. Its statistical approximation is with
t1: acceleration time
t2: run time
t3: deceleration time
t4: time in a move
4
3
2
1
3
2
F
L
J
2
2
F
L
1
2
P
RMS
t
t
t
t
t
T
T
T
t
T
T
t
T
T