172-65132MA-07 (JX Series) 16 Feb 2022
5
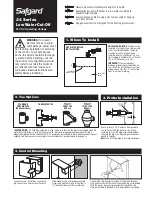
Operation
Principles of air and condensate discharge:
1. Initial Air and Cold Condensate Discharge
At startup, before steam is supplied, the trap is
cold so the X-element is contracted and the air
vent valve seat (A) is open. This allows for the
rapid discharge of air through the air vent valve
(A) and cold condensate through the orifice (B),
when steam is first supplied to the system.
2. Condensate Discharge
After the discharge of initial air and cold
condensate, the heat of the inflowing steam and
condensate causes the X-element to expand,
closing the air vent valve (A). The rising
condensate level causes the float to rise due to
buoyancy, opening the orifice (B) and allowing
condensate to be discharged.
3. Hot Air Discharge
Should hot air flow into the trap with the steam
during normal operation, the temperature of the X-
element drops, causing it to momentarily contract
and open the air vent valve (A), which allows for
the rapid discharge of the air. After the air is
discharged and steam contacts the
X-element, the temperature will increase causing
the air vent valve (A) to close.
4. Closed Position
When the condensate flow rate decreases, the
float falls as condensate is discharged, closing off
the orifice (B). A water seal is maintained at all
times over the orifice (B) to prevent steam loss.
Note: the high steam temperature causes the
X-element to expand, keeping the air vent closed.
Air
Steam
Condensate