4–12
CMCLK
CSCLK
Codec Master Clock 2.048 MHz
Codec Sample Clock 8 kHz
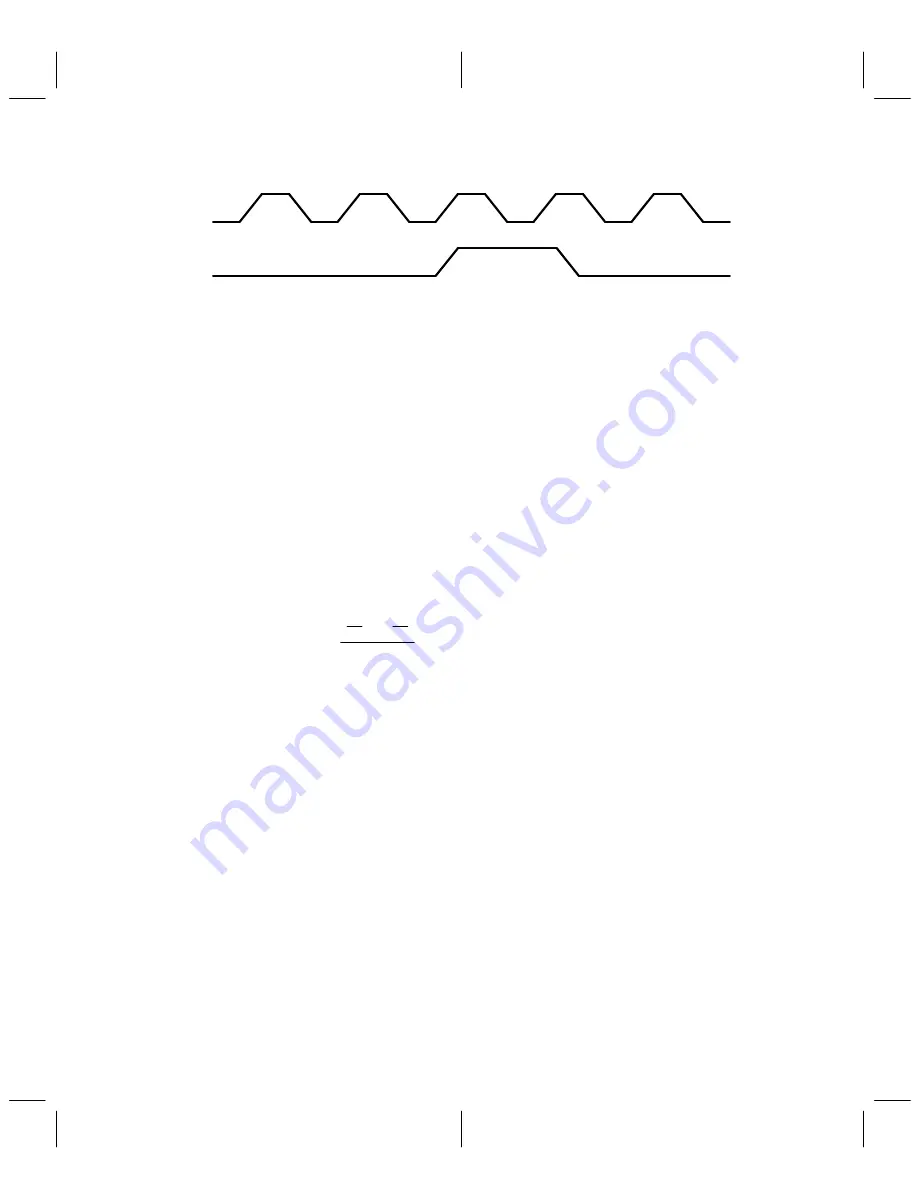
Figure 4–4. Codec Master and Sample Clock Timing
4.11.1
Clock Generation
There are three options for generating the master clock. A fundamental crystal or a third-overtone crystal
with a frequency of 38.88 MHz can be connected between the MCLKIN and the XTAL terminals or an
external clock source can be connected directly to the MCLKIN terminal. The MCLKOUT is a buffered
master clock output at the same frequency as MCLKIN. MCLKOUT can be used as the source clock for other
devices in the system. Setting the MCLKEN bit in the MStatCtrl register enables or disables this output. The
MCLKOUT enable is synchronous with MCLKIN to eliminate abnormal cycles of the clock output.
All output clocks are derived from the master clock (MCLKIN). The sample clocks for the digital and analog
modes, the 8-kHz speech codec sample clock, and the clocks for the A/D and D/A functions are also derived
from the master clock.
4.11.2
Speech-Codec Clock Generation
The TCM4300 generates two clock outputs for use with speech codecs: the 2.048-MHz CMCLK and the
8-kHz CSCLK. These clocks are generated so that each CSCLK period contains exactly 256 cycles of
CMCLK. Since 2.048 MHz is not an integer division of the 38.88-MHz MCLKIN, one out of every 64 CMCLK
cycles is 18 MCLKIN periods long, and the remaining 63 out of 64 are 19 MCLKIN periods long. The average
frequency of MCLKIN is therefore
MCLKIN
ǒ
63
19
)
1
18
Ǔ
64
+
2.048092 MHz
CSCLK is exactly CMCLK divided by 256 (see Figure 4–4).
To save power, the codec clocks are only generated by TCM4300 when the SCEN bit of the DStatCtrl
register is set high. When SCEN is low, both outputs, CSCLK and CMCLK, are held low. SCEN is also
available as an output.
4.11.3
Microcontroller Clock
A variable modulus divider provides a selection of frequencies for use as a microcontroller clock. The master
clock is divided by an integer from 32 to 2, giving a wide range of frequencies available to the microcontroller
(1.215 MHz to 19.88 MHz). The modulus can be changed by writing to the microcontroller clock register.
The output duty cycle is within the requirements of most microcontrollers, that is, from 40% to 60%. At
power-on reset, the clock divider defaults to 1.215 MHz.
4.11.4
Sample Interrupt SINT
The SINT interrupt signal is the primary timing signal for the TCM4300 interface. The primary function of
the SINT is to indicate the ready condition to receive or transmit data. It also conveys timing marks to allow
for the synchronization of system DSP functions. In the digital mode, SINT is used in conjunction with the
received sync word to track cellular system timing. The SINT can be disabled by writing a 1 to the SDIS bit
of the DIntCtrl register. When enabled, the SINT operates continuously at 48.6 kHz in the digital mode and
at 40 kHz in the analog mode. The SINT signal does not require an interrupt acknowledge. The SINT is active
low for 5.5 MCLK cycles (141.5 ns) in the analog mode and 6.5 MCLK cycles (167.2 ns) in the digital mode.
Summary of Contents for TCM4300
Page 1: ...Data Manual 1996 Mixed Signal Products...
Page 2: ...Printed in U S A 10 96 SLWS010F...
Page 23: ...2 8...
Page 35: ...3 12...
Page 67: ...4 32...






























