GUI Application
7
SLOU536 – June 2020
Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DRV8428EVM GUI User's Guide
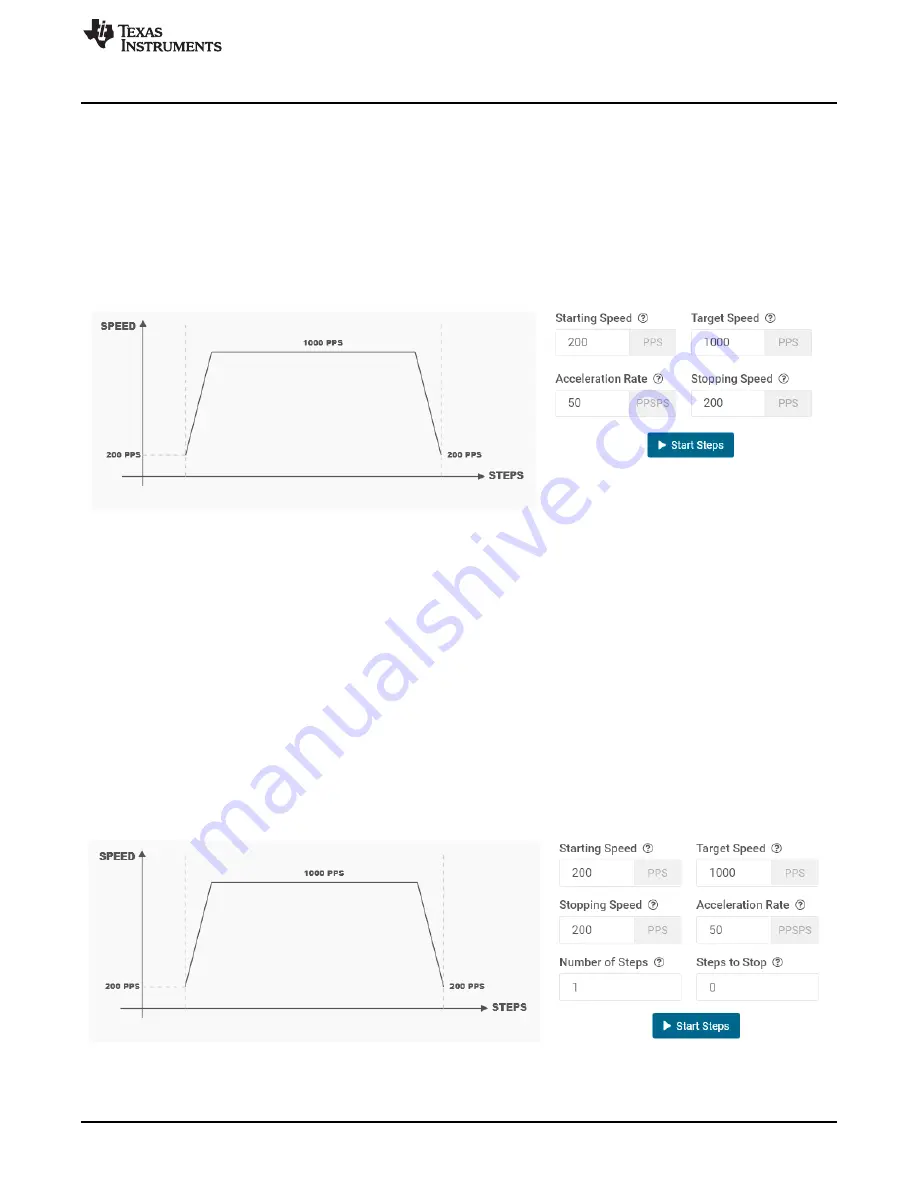
The 'Start Steps' command computes how frequently automatic speed updates are issued and a second
timer is used to change the speed according to the programmed acceleration rate profile. Once clicked,
the motor will begin spinning according to the parameters set in the GUI.
When the target speed PPS value is reached, the acceleration profile ends and the motor continues
running until the 'Stop Steps' button is clicked. When the stepper is commanded to stop, the controller
performs the same actions as it did while accelerating, but in reverse order to decelerate until the stop
speed PPS value is reached, in which case the motor fully stops.
shows the acceleration profile and the role each parameter plays during speed computation.
Figure 6. Controls Available for Speed Mode
3.3.1.1.2
Step Mode
Step Mode allows the user to move the stepper motor a configured number of steps. Stepper controls are
enabled only when ‘Motor Driver' control is enabled. ‘Start Steps’ button is enabled only when ‘Driver
Outputs' control is enabled for example, EN/nFault pin is set to high. When the ‘Start Steps’ button is
clicked, the motor starts spinning at the starting speed and accelerates at the rate configured to reach until
the number of steps is reached after which it stops.
The acceleration and deceleration profiles work similarly as before, except when the deceleration routine
starts and when the motor stops are a function of the 'Steps to Stop' and deceleration rate parameters.
The configuration can be visualized in the graph embedded in the GUI. If the "Reciprocate" button is
enabled, the stepper will travel the set number of steps, then reverse direction. It will do this continuously
until 'Stop Steps' is clicked.
shows the controls available in Step Mode.
Figure 7. Controls Available for Step Mode
































