F97CMN and G97CMN: Installation, Start-up, Operating and Service and Maintenance Instructions
Manufacturer reserves the right to change, at any time, specifications and designs without notice and without obligations.
70
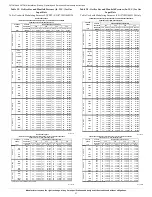
Two-Stage Thermostat and Two-Stage Intermediate/
Maximum Heating
See
for thermostat connections
NOTE:
In this mode the intermediate-heat only switch SW4-2 must be
ON to select the intermediate-heat only operation mode in response to
closing the thermostat R to W1 circuit. Closing the thermostat R to
W1-and-W2 circuits always causes maximum-heat operation, regardless
of the setting of the intermediate-heat only switch.
The wall thermostat ”calls for heat”, closing the R to W1 circuit for
intermediate-heat or closing the R to W1-and-W2 circuits for
maximum-heat. The furnace control performs a self-check, and verifies
the low, medium and high pressure switch contacts LPS, MPS and HPS
are open , then de-energizes the PSR relay to close the NC contact.
The start up and shut down functions and delays described above apply
to the two-stage intermediate/maximum heating mode as well, except for
switching from maximum- to intermediate-heat.
1.
Switching from Maximum- to Intermediate-Heat
—
If the
thermostat R to W2 circuit opens, and the R to W1 circuit remains
closed, the furnace control CPU will gradually decrease the inducer
motor speed to the required intermediate-heat RPM. When the
inducer motor IDM reduces pressure sufficiently, the high pressure
switch HPS will open and the gas rate will be changed to
intermediate-heat. When the inducer motor speed gets within 15%
of the required intermediate-heat RPM the furnace control CPU
will start a 5 second blower airflow change delay. After the 5
second blower airflow change delay is completed the blower
airflow will transition to intermediate-heat airflow.
Cooling Mode
The thermostat “calls for cooling.”
1.
Single-Speed Cooling
See
for thermostat connections.
The thermostat closes the R to G-and-Y circuits. The R to Y circuit starts
the outdoor unit, and the R to G-and-Y/Y2 circuits start the furnace
blower motor BLWM on cooling airflow. Cooling airflow is based on the
A/C selection shown in
The electronic air cleaner terminal EAC-1 is energized with 115 vac
when the blower motor BLWM is operating. When the thermostat is
satisfied, the R to G-and-Y circuits are opened. The outdoor unit will
stop, and the furnace blower motor BLWM will continue operating at
cooling airflow for an additional 90 seconds. Jumper Y/Y2 to DHUM to
reduce the cooling off-delay to 5 seconds, see
2.
Two Stage Thermostat and Two-Speed Cooling
See
for thermostat connections.
The thermostat closes the R to G-and-Y1 circuits for low cooling or
closes the R to G-and-Y1-and-Y2 circuits for high cooling. The R to Y1
circuit starts the outdoor unit on low cooling speed, and the R to
G-and-Y1 circuit starts the furnace blower motor BLWM at low-cooling
airflow which is the SW3 selection as shown in
. The R to
Y1-and-Y2 circuits start the outdoor unit on high-cooling speed, and the
R to G-and-Y/Y2 circuits start the furnace blower motor BLWM at
high-cooling airflow. High-cooling airflow is based on the A/C selection
shown in
The electronic air cleaner terminal EAC-1 is energized with 115 vac
whenever the blower motor BLWM is operating.
When the thermostat is satisfied, the R to G-and-Y1 or R to
G-and-Y1-and-Y2 circuits are opened. The outdoor unit stops, and the
furnace blower BLWM and electronic air cleaner terminal EAC-1 will
remain energized for an additional 90 seconds. Jumper Y1 to DHUM to
reduce the cooling off-delay to 5 seconds, see
3.
Dehumidification Mode
See
for thermostat connections.
The dehumidification output, D or DHUM on the Thermostat should be
connected to the furnace control thermostat terminal DHUM. When
there is a dehumidify demand, the DHUM input is activated, which
means 24 vac signal is removed from the DHUM input terminal. In other
words, the DHUM input logic is reversed. The DHUM input is turned
ON when no dehumidify demand exists. Once 24 vac is detected by the
furnace control, dehumidification capability is activated. If the DHUM
input is removed for more than 48 hours, the furnace control reverts back
to non-dehumidification mode.
The cooling operation described above in the Cooling Mode section also
applies to Dehumidification mode. The exceptions are listed below:
a.
Low cooling
– When the R to G-and-Y1 circuit is closed and
there is a demand for dehumidification, the furnace blower motor
BLWM will drop the blower airflow to 86% of low cooling
airflow which is the SW3 selection as shown in
a.
High cooling
– When the R to G-and Y/Y2 circuit is closed and
there is a demand for dehumidification, the furnace blower motor
BLWM will drop the blower airflow to 86% of high-cooling
airflow. High-cooling airflow is based on the A/C selection
shown in
b.
Cooling off-delay
– When the “call for cooling” is satisfied and
there is a demand for dehumidification, the cooling blower-off
delay is decreased from 90 seconds to 5 seconds.
Continuous Blower Mode
When the R to G circuit is closed by the thermostat, the blower motor
BLWM will operate at continuous blower airflow. Continuous blower
airflow selection is initially based on the SW3 selection shown in
. Factory default is shown in
. Terminal EAC-1 is
energized as long as the blower motor BLWM is energized.
During a call for heat, the furnace control CPU will transition the blower
motor BLWM to continuous blower airflow, minimum-heat airflow, or
the mid-range airflow, whichever is lowest. The blower motor BLWM
will remain ON until the main burners ignite then shut OFF and remain
OFF for the blower-ON delay (45 seconds in intermediate heat, and 25
seconds in maximum-heat), allowing the furnace heat exchangers to heat
up more quickly, then restarts at the end of the blower-ON delay period
at modulating or maximum-heat airflow respectively.
The blower motor BLWM will revert to continuous-blower airflow after
the heating cycle is completed. When the thermostat satisfies, the
furnace control CPU will drop the blower motor BLWM to
minimum-heat airflow during the selected blower-OFF delay period
before transitioning to continuous-blower airflow.
When the thermostat “calls for low-cooling”, the blower motor BLWM
will operate at low-cooling airflow. When the thermostat is satisfied, the
blower motor BLWM will operate an additional 90 seconds at
low-cooling airflow before transitioning back to continuous-blower
airflow.
When the thermostat “calls for high-cooling”, the blower motor BLWM
will operate at high cooling airflow. When the thermostat is satisfied, the
blower motor BLWM will operate an additional 90 seconds at
high-cooling airflow before transitioning back to continuous-blower
airflow.
When the R to G circuit is opened, the blower motor BLWM will
continue operating for an additional 5 seconds, if no other function
requires blower motor BLWM operation.
Heat Pump
See
for thermostat connections. When installed with a heat
pump, the furnace control automatically changes the timing sequence to
avoid long blower off times during demand defrost cycles. Whenever
W/W1 is energized along with Y1 or Y/Y2, the furnace control CPU will
transition to or bring on the blower motor BLWM at cooling airflow,
minimum-heat airflow, or the mid-range airflow, whichever is lowest.