27
Explanation of terms, useful information
CD
A Compact Disc (CD) is a digital data medium which
requires a little care in handling:
•
The surface of a CD may only be
cleaned using a soft, dry cloth. Wipe in
straight lines from the centre towards
the edge.
•
Never use petrol, paint thinners, disc cleaning fluids
or similar agents.
•
CDs must be handled with care to avoid major
damage to the surface. Severely scratched surfaces,
writing on the discs, or sticking labels on the discs
may result in a CD which can no longer be read.
•
CDs should not be heated or bent. Choose a storage
site which fulfils these requirements.
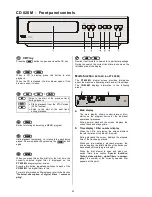
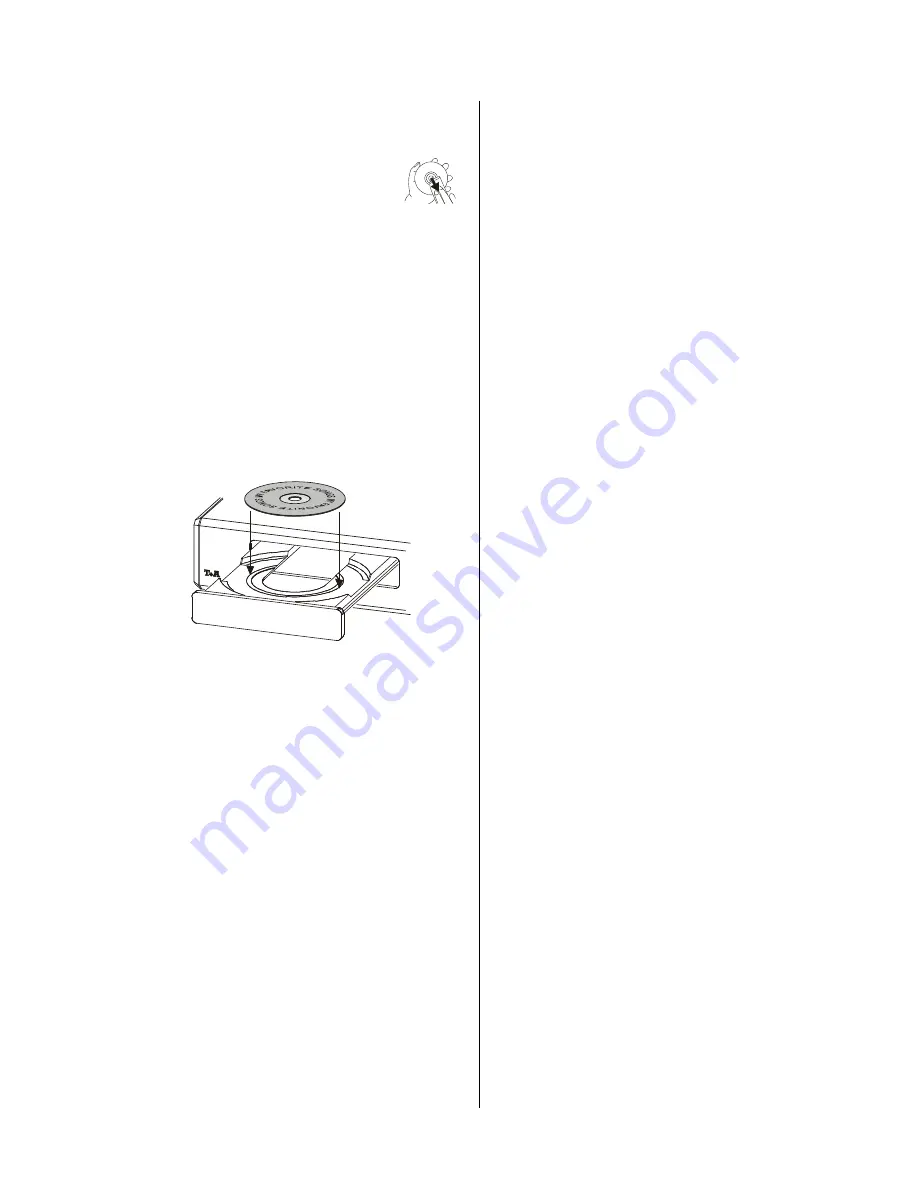
CD SINGLES
CD singles are discs of smaller diameter and
correspondingly shorter playing time. The
CD 820 M
is
capable of playing CD singles. To load a CD single place
the disc in the circular depression in the centre of the
drawer.
DSP (D
igital
S
ignal
P
rocessor)
The
CD 820 M
features a freely programmable signal
processor. A DSP can process digital signals in any way,
and that is why they allow better oversampling rates than
standard modules.
TOC
Internal index (TABLE OF CONTENT) of a CD.
If the TOC area of a CD is unreadable due to damage,
scratches etc., the entire CD is rendered unusable.
TRACK
Track is another termed used for a title on a CD. The
tracks and their duration are stated on the CD sleeve.
Technical description
Digital filters / Oversampling
The audio data on CDs is stored at a sampling rate of
44.1 - i.e. for each second of music 44.100 sampled
values are available for each channel. In the
CD 820 M
the audio data read from the CD is „multiplied“ to a
higher sampling rate (352,8 kHz) before it is converted
back into analogue music signals. This process delivers
a very much better, more finely graduated signal to the
converter,
which
can
then
be
converted
with
correspondingly higher precision. The raised sampling
rate is a calculating process for which there are many
different mathematical methods. In almost all digital
audio devices which exploit the advantages of increased
digital sampling rate a process known as a FIR filter is
employed for this purpose. At
we have been
carrying out research for more than ten years, aimed at
improving the oversampling process, because the
standard FIR method has one drawback to set against its
indisputable advantages: it adds small pre- and post-
echoes to the music signals. At
we have developed
mathematical processes (known as Bezier polynomial
interpolators) which do not share this disadvantage. For
this reason they should sound better and more natural
than the usual standard process. Since the calculating
procedure employed by us is considerably more complex
than the standard method, the
CD 820 M
features a
high-performance digital signal processor (DSP) which
carries out the over-sampling process with immense
precision (56 bit) using special algorithms developed by
.
The freely programmable DSP which we use is capable
of carrying out the oversampling process using any
method of calculation. For this reason we have
implemented two slightly modified Bezier processes
(filters 3 and 5) in the
CD 820 M
in addition to the pure
Bezier process (filter 4), together with two variants of the
standard process (filter 1 and filter 2). For more
information on the five different processes please refer to
the next section. You can switch between the various
algorithms using the
button on the front panel, or
the
button on the remote control handset, then
decide for yourself which of the filters gives the results
you prefer.