Powering On the Welder
When
all of the previous setup steps
in this manual are complete the welder can be powered on.
1. Ensure that the power cord is connected to the power cord socket and the supply power.
2. Check the 10A fuse below the ON/OFF switch located on the back of the unit.
3. Use the ON/OFF switch to power the unit on.
Voltage Selection
•
The voltage is determined by the diameter of the stud and the base material thickness. The unit is
programmed with the recommended voltage settings for various stud sizes.
Fine tuning the volt-
age for each application from this starting point is recommended.
•
Setting the required weld voltage is achieved by selecting the desired stud size on the screen or
manually setting the voltage by using the
+
or
-
arrows.
•
Fast voltage selection can be done from the voltage mode screen. This will replace the preset val-
ues on the screen with voltages in increments of 10V and can be manually adjusted by using the
arrows.
Testing the Weld Settings
1. After performing all of the setup steps listed in this manual, it is recommended that several test
welds be performed with the same diameter stud and base material used for the application. This
will verify that all of the settings are correct to achieve the desired results.
2. Welding is done by placing the stud into the collet and pressing the stud gun to the work piece.
3. Hold the gun perpendicular to the work piece, align the stud to the desired location, press down
so that the foot piece is flush with the base material, and squeeze the trigger.
4. Spreading the collet tines when lifting the stud gun from the welded stud will shorten the life of
the collet and will eventually create an undesirable weld.
For maximum collet life remove the
stud gun from the welded stud by pulling the stud gun straight off of the welded stud.
5. Properly welded studs are tested by either torqueing or bending the stud. Using either method
the threaded portion of the stud may break. However, the welded flange of the stud should stay
in place. Additionally, if the base material is very thin, a full slug the diameter of the flange will
pull from the base metal.
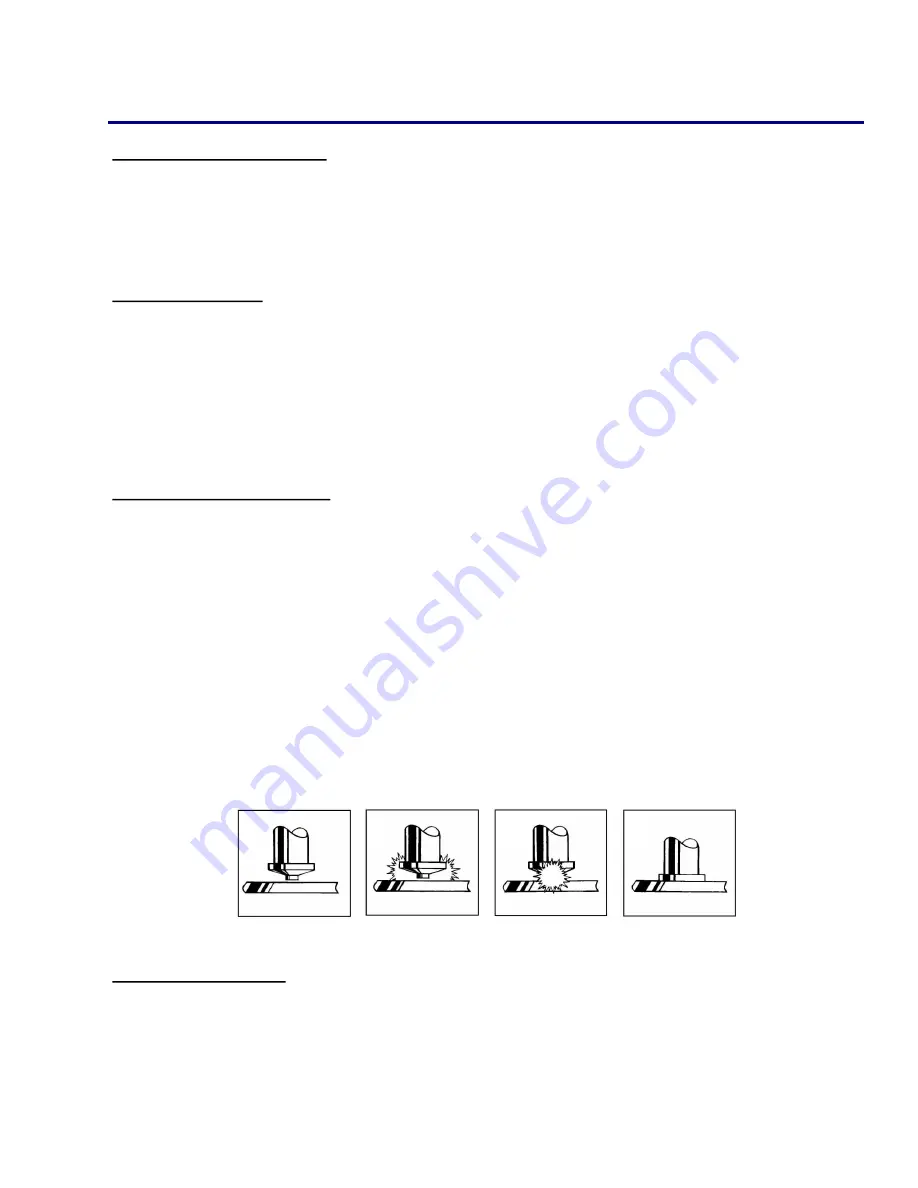
Inspecting the Weld
1. Visually inspect the weld. If there is a significant amount of splatter then the weld is too hot, lower
the voltage. If there is no splatter then the weld is too cold, increase the voltage.
2. A good weld will result in a small, visible, and 360° flashing surrounding the flange of the stud. If
there is weld flash on only one side of the base of the flange, this is called “arc blow,” and can be
solved by repositioning the ground clamp or using a dual ground clamp.
SETUP AND WELDING
11
WWW.STUDWELDPROD.COM
800-252-1919

















