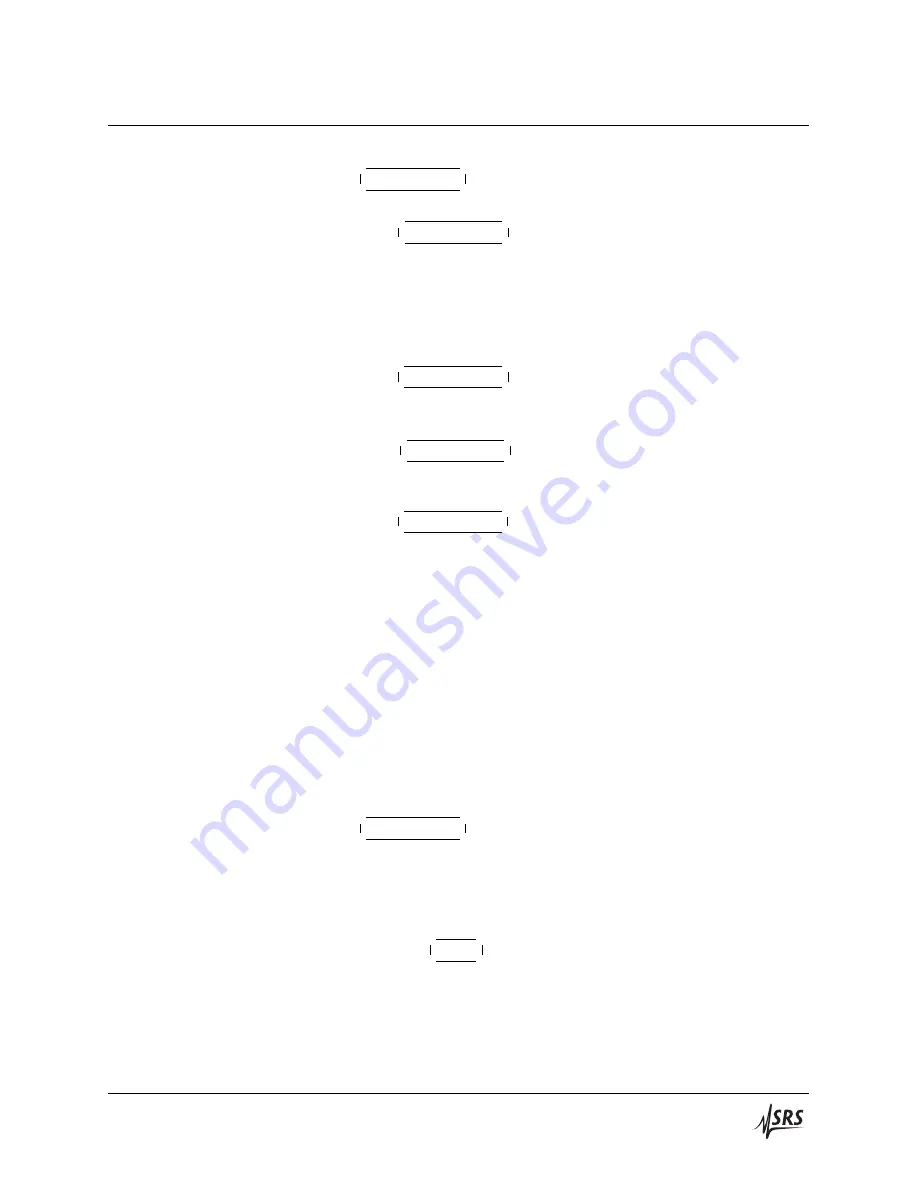
1.8
Reference oscillator external input
1 – 7
2. Press [Ampl] in the Reference section,
and turn the
REFERENCE knob counterclockwise until the numeric dis-
play shows 95.0 mV.
3. Turn
SENSITIVITY 2 clicks counterclockwise, to 100 mV. The
meter should read near
+
95% deflection
4. Enable the output o
ff
set by pressing [On
/
O
ff
] in the OFFSET
block. Perform an auto-o
ff
set adjustment by pressing [O
ff
set]
in the AUTO block. After the pause, the o
ff
set should show a
value near
+
95% o
ff
set. The panel meter should read near zero.
5. Turn
SENSITIVITY 2 more clicks counterclockwise, to 20 mV.
The panel meter should still read near zero, while the REFER-
ENCE display shows a value near
+
475%.
6. Turn
SENSITIVITY 1 click counterclockwise, to 10 mV. The
REFERENCE display should read near
+
950%, and the panel
meter should still be near null.
7. Turn
SENSITIVITY 1 click further counterclockwise. The dis-
play should show the message “Attn OFFSt”, and the
OFFSET
annunciator in the REFERENCE display block should blink.
The sensitivity does not change.
8. Press the [Ampl] button, and reduce the amplitude to 90.0 mV.
The panel meter should show around
−
50% full scale deflec-
tion.
9. Press the [O
ff
set] button in the AUTO block again, to automati-
cally re-adjust the o
ff
set. The REFERENCE display should now
show near
+
900%, and the panel meter should be nulled.
1.8
Reference oscillator external input
1. Restore
default
settings
by
pressing
[Recall];
turn
REFERENCE if necessary to display ”deFLt”, and then
press [Recall] again.
2. Set the function generator to produce a 1 Vrms, 2 kHz sine wave.
Connect the function generator output to the SR124 “Ext. In”
BNC, in the REFERENCE section.
3. Turn the
Mode knob in the REFERENCE section one click
clockwise, to the
f External
setting. The
Unlocked
indicator
should illuminate for between 5 and 20 seconds, and then the
SR124 should lock to the external signal.
4. Press [Freq] in the REFERENCE section to perform an oscillator
frequency measurement. After a brief delay, the REFERENCE
SR124
Analog Lock-In Amplifier






























