– 2 –
SAFETY-RELATED COMPONENT WARNING!!
COMPONENTS IDENTIFIED BY MARK
!
OR DOTTED
LINE WITH MARK
!
ON THE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS
AND IN THE PARTS LIST ARE CRITICAL TO SAFE
OPERATION. REPLACE THESE COMPONENTS WITH
SONY PARTS WHOSE PART NUMBERS APPEAR AS
SHOWN IN THIS MANUAL OR IN SUPPLEMENTS PUB-
LISHED BY SONY.
WARNING!!
WHEN SERVICING, DO NOT APPROACH THE LASER
EXIT WITH THE EYE TOO CLOSELY. IN CASE IT IS
NECESSARY TO CONFIRM LASER BEAM EMISSION,
BE SURE TO OBSERVE FROM A DISTANCE OF
MORE THAN 25 cm FROM THE SURFACE OF THE
OBJECTIVE LENS ON THE OPTICAL PICK-UP BLOCK.
CAUTION:
The use of optical instrument with this product will increase eye
hazard.
CAUTION
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures
other than those specified herein may result in hazardous ra-
diation exposure.
1. Check the area of your repair for unsoldered or poorly-sol-
dered connections. Check the entire board surface for solder
splashes and bridges.
2. Check the interboard wiring to ensure that no wires are
“pinched” or contact high-wattage resistors.
3. Look for unauthorized replacement parts, particularly transis-
tors, that were installed during a previous repair. Point them
out to the customer and recommend their replacement.
4. Look for parts which, though functioning, show obvious signs
of deterioration. Point them out to the customer and recom-
mend their replacement.
5. Check the line cord for cracks and abrasion. Recommend the
replacement of any such line cord to the customer.
6. Check the B+ voltage to see it is at the values specified.
7. Check the antenna terminals, metal trim, “metallized” knobs,
screws, and all other exposed metal parts for AC leakage.
Check leakage as described below.
SAFETY CHECK-OUT
After correcting the original service problem, perform the following
safety checks before releasing the set to the customer:
LEAKAGE TEST
The AC leakage from any exposed metal part to earth ground
and from all exposed metal parts to any exposed metal part having
a return to chassis, must not exceed 0.5 mA (500 microamperes).
Leakage current can be measured by any one of three methods.
1. A commercial leakage tester, such as the Simpson 229 or RCA
WT-540A. Follow the manufacturers’ instructions to use these
instruments.
2. A battery-operated AC milliammeter. The Data Precision 245
digital multimeter is suitable for this job.
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by means of a
VOM or battery-operated AC voltmeter. The “limit” indica-
tion is 0.75V, so analog meters must have an accurate low-
voltage scale. The Simpson 250 and Sanwa SH-63Trd are
examples of a passive VOM that is suitable. Nearly all bat-
tery operated digital multimeters that have a 2V AC range are
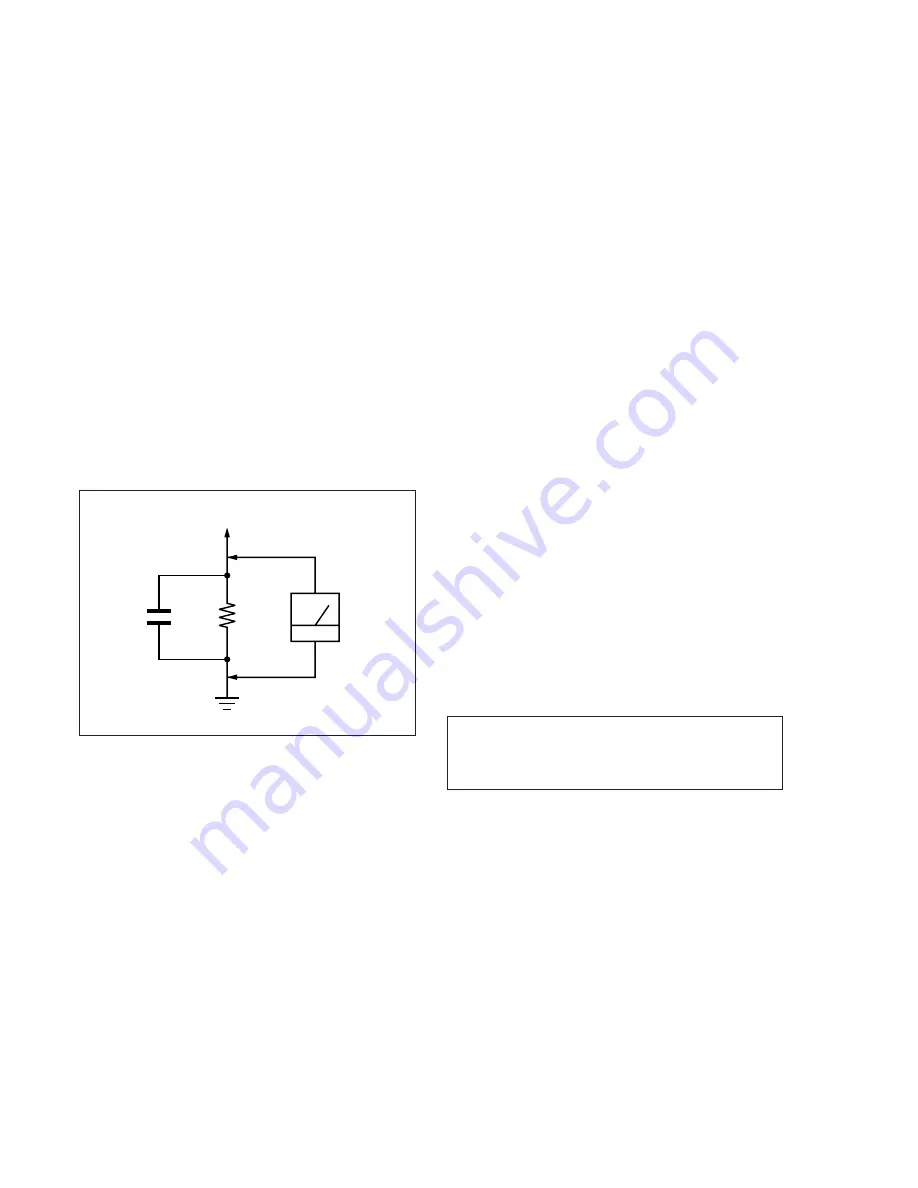
suitable. (See Fig. A)
Fig. A
Using AC voltmeter to check AC leakage
1.5 k
Ω
0.15
µ
F
AC
Voltmeter
(0.75 V)
To Exposed Metal
Parts on Set
Earth Ground
Summary of Contents for DVP-S300
Page 12: ...1 2 ...
Page 13: ...1 3 ...
Page 14: ...1 4 ...
Page 15: ...1 5 ...
Page 16: ...1 6 ...
Page 17: ...1 7 ...
Page 18: ...1 8 ...
Page 19: ...1 9 ...
Page 20: ...1 10 1 10 E ...
Page 49: ...7 5 E 1 2 10 12 14 24 25 CN252 MB 78 BOARD Side B ...




















