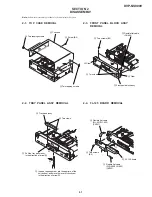
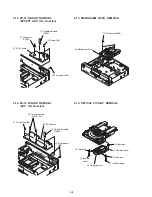
1-24
98
DTS (page 25, 89)
Digital audio compression technology that
Digital Theater Systems, Inc. developed.
This technology conforms to 5.1-channel
surround sound. The rear channel is stereo
and there is a discrete subwoofer channel in
this format. DTS provides the same 5.1
discrete channels of high quality digital
audio.
Good channel separation is realized because
all of the channel data is recorded discretely
and little deterioration is realized because all
channel data processing is digital.
DVD VIDEO (page 6)
A disc that contains up to 8 hours of moving
pictures even though its diameter is the same
as a CD.
The data capacity of a single-layer and
single-sided DVD is 4.7 GB (Giga Byte),
which is 7 times that of a CD. The data
capacity of a double-layer and single-sided
DVD is 8.5 GB, a single-layer and double-
sided DVD is 9.4 GB, and double-layer and
double-sided DVD is 17GB.
The picture data uses the MPEG 2 format,
one of the worldwide standards of digital
compression technology. The picture data is
compressed to about 1/40 (average) of its
original size. The DVD also uses a variable
rate coding technology that changes the data
to be allocated according to the status of the
picture. Audio information is recorded in a
multi-channel format, such as Dolby Digital,
allowing you to enjoy a more real audio
presence.
Furthermore, various advanced functions
such as the multi-angle, multilingual, and
Parental Control functions are provided with
the DVD.
DVD-RW (page 6)
A DVD-RW is a recordable and rewritable
disc with the same size as the DVD VIDEO.
The DVD-RW can be recorded in two
different modes: VR mode and Video mode.
VR (Video Recording) mode enables various
programming and editing functions, some of
which are limited in the case of Video mode.
Video mode complies with DVD VIDEO
format and is compatible with DVD players
while a DVD-RW recorded in VR mode can
only be played on DVD-RW compliant
players. The
“
DVD-RW
”
appears in this
manual, or the on-screen display refers to
DVD-RWs in VR mode.
Film based software (page 85)
DVDs can be classified as Film based or
Video based software. Film based DVDs
contain the same images (24 frames per
second) that are shown at movie theaters.
Interlace format (page 84)
Interlace format shows every other line of an
image as a single
“
field
”
and is the standard
method for displaying images on television.
The even number field shows the even
numbered lines of an image, and the odd
numbered field shows the odd numbered
lines of an image.
Index (SACD/CD)/Video Index (VIDEO CD)
(page 9)
A number that divides a track into sections to
easily locate the point you want on an SACD/
CD or VIDEO CD. Depending on the disc, no
index may be recorded.
Parental Control (page 72)
A function of the DVD used to limit playback
of the disc according to the age of the user
and the limitation level in each country. The
limitation varies from disc to disc; when it is
activated, or playback is completely
prohibited, violent scenes are skipped or
replaced with other scenes, etc.
Additional Infor
m
a
tio
n
99
Progressive format (page 84)
Compared to the Interlace format that
alternately shows every other line of an
image (field) to create one frame, the
Progressive format shows the entire image at
once as a single frame. This means that while
the Interlace format can show 30 frames (60
fields) in one second, the Progressive format
can show 60 frames in one second. The
overall picture quality increases and still
images, text, and horizontal lines appear
sharper. This player is compatible with the
480 progressive format.
Region Code (page 6)
This system is used to protect the copyrights.
A region number is allocated on each DVD
player or DVD disc according to the sales
region. Each region code is shown on the
player as well as on the disc packaging. The
player can play the discs that match its region
code. The player can also play discs with the
mark. Even when the region code is not
shown on the DVD, the region limit may still
be activated.
Scene (page 9)
On a VIDEO CD with PBC (playback
control) functions, the menu screens, moving
pictures and still pictures are divided into
sections called
“
scenes.
”
Super Audio CD (SACD) (page 6)
An SACD disc can reproduce sounds that are
extremely faithful to the original sound by
use of DSD (Direct Stream Digital)
technology. This technology utilizes a
sampling frequency of 2.8224 MHz, which is
64 times that of a conventional CD, and 1-bit
quantization that enables the disc to hold 4
times the amount of information that a
standard PCM format CD can hold. SACDs
are divided into the following types.
•
Super Audio CD (single layer disc)
This disc consists of a single HD layer*.
* High density signal layer for the Super
Audio CD
•
Super Audio CD (dual layer disc)
This disc consists of dual HD layers and is
capable of extended play over long periods.
Also, as the dual layer disc consists of dual
HD layers on one side only, you do not have
to turn the disc over during playback.
•
Super Audio CD + CD (Hybrid disc)
This disc consists of an HD layer and a CD
layer. Also, as the dual layers are on one
side only, you do not have to turn the disc
over during playback. You can play the CD
layer using a conventional CD player.
ALL
HD (high density) layer
HD layer
HD layer
CD layer
HD layer
continued
100
•
2 c Multi-channel Super Audio CD
This disc consists of the 2 channel playback
area and the multi-channel playback area.
Title (page 9)
The longest section of a picture or music
feature on a DVD, movie, etc., in video
software, or the entire album in audio
software.
Track (page 9)
Sections of a picture or a music feature on an
SACD/CD or VIDEO CD (the length of a
song).
TV Virtual Surround (TVS) (page 60)
Technology from Sony developed to produce
surround sound for home use using just a
stereo TV. Designed to work with the sound
characteristics of your TV, this technology
brings the excitement of surround sound to
your home using nothing more than your
stereo TV
’
s internal speakers. Furthermore,
various TVS modes are available. For
example,
“
TVS WIDE
”
uses just two
speakers to create a virtual sound
environment that makes you feel like you are
surrounded by multiple speakers.
Video based software (page 84)
DVDs can be classified as Film based or
Video based software. Television dramas or
sit-coms are examples of Video based
software and display images at 30 frames (or
60 fields) per second.
2 channel playback area
Multi-channel playback
area
102
Language Code List
For details, see pages 58, 65, 81.
The language spellings conform to the ISO 639: 1988 (E/F) standard.
Code Language
Code Language
Code Language
Code Language
1027 Afar
1028 Abkhazian
1032 Afrikaans
1039 Amharic
1044 Arabic
1045 Assamese
1051 Aymara
1052 Azerbaijani
1053 Bashkir
1057 Byelorussian
1059 Bulgarian
1060 Bihari
1061 Bislama
1066 Bengali;
Bangla
1067 Tibetan
1070 Breton
1079 Catalan
1093 Corsican
1097 Czech
1103 Welsh
1105 Danish
1109 German
1130 Bhutani
1142 Greek
1144 English
1145 Esperanto
1149 Spanish
1150 Estonian
1151 Basque
1157 Persian
1165 Finnish
1166 Fiji
1171 Faroese
1174 French
1181 Frisian
1183 Irish
1186 Scots Gaelic
1194 Galician
1196 Guarani
1203 Gujarati
1209 Hausa
1217 Hindi
1226 Croatian
1229 Hungarian
1233 Armenian
1235 Interlingua
1239 Interlingue
1245 Inupiak
1248 Indonesian
1253 Icelandic
1254 Italian
1257 Hebrew
1261 Japanese
1269 Yiddish
1283 Javanese
1287 Georgian
1297 Kazakh
1298 Greenlandic
1299 Cambodian
1300 Kannada
1301 Korean
1305 Kashmiri
1307 Kurdish
1311 Kirghiz
1313 Latin
1326 Lingala
1327 Laothian
1332 Lithuanian
1334 Latvian; Lettish
1345 Malagasy
1347 Maori
1349 Macedonian
1350 Malayalam
1352 Mongolian
1353 Moldavian
1356 Marathi
1357 Malay
1358 Maltese
1363 Burmese
1365 Nauru
1369 Nepali
1376 Dutch
1379 Norwegian
1393 Occitan
1403 (Afan)Oromo
1408 Oriya
1417 Punjabi
1428 Polish
1435 Pashto; Pushto
1436 Portuguese
1463 Quechua
1481 Rhaeto-
Romance
1482 Kirundi
1483 Romanian
1489 Russian
1491 Kinyarwanda
1495 Sanskrit
1498 Sindhi
1501 Sangho
1502 Serbo-Croatian
1503 Singhalese
1505 Slovak
1506 Slovenian
1507 Samoan
1508 Shona
1509 Somali
1511 Albanian
1512 Serbian
1513 Siswati
1514 Sesotho
1515 Sundanese
1516 Swedish
1517 Swahili
1521 Tamil
1525 Telugu
1527 Tajik
1528 Thai
1529 Tigrinya
1531 Turkmen
1532 Tagalog
1534 Setswana
1535 Tonga
1538 Turkish
1539 Tsonga
1540 Tatar
1543 Twi
1557 Ukrainian
1564 Urdu
1572 Uzbek
1581 Vietnamese
1587 Volapük
1613 Wolof
1632 Xhosa
1665 Yoruba
1684 Chinese
1697 Zulu
1703 Not specified