KDL-40NX725/46NX725
7
SECTION 1 - SAFETY AND FEATURES
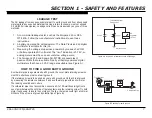
LEAKAGE TEST
The AC leakage from any exposed metal part to earth ground and from all exposed
metal parts to any exposed metal part having a return to chassis, must not exceed
0.5 mA(500 microamperes). Leakage current can be measured by any one of three
methods.
1. A commercial leakage tester, such as the Simpson 229 or RCA
WT-540A. Follow the manufacturers’ instructions to use these
instructions.
2. A battery-operated AC milliampmeter. The Data Precision 245 digital
multimeter is suitable for this job.
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by means of a VOM
or battery-operated AC voltmeter. The “limit” indication is 0.75 V, so
analog meters must have an accurate low voltage scale.
4. The Simpson’s 250 and Sanwa SH-63TRD are examples of
passive VOMs that are suitable. Nearly all battery-operated digital
multimeters that have a 2 VAC range are suitable (see Figure A).
HOW TO FIND A GOOD EARTH GROUND
A cold-water pipe is a guaranteed earth ground; the cover-plate retaining screw on
most AC outlet boxes is also at earth ground.
If the retaining screw is to be used as your earth ground, verify that it is at ground
by measuring the resistance between it and a cold-water pipe with an ohmmeter.
The reading should be zero ohms.
If a cold-water pipe is not accessible, connect a 60-to 100-watt trouble-light (not a
neon lamp) between the hot side of the receptacle and the retaining screw. Try both
slots, if necessary, to locate the hot side on the line; the lamp should light at normal
brilliance if the screw is at ground potential (see Figure B).
Trouble Light
AC Outlet Box
Ohmmeter
Cold-water Pipe
Figure B. Checking for earth ground.
To Exposed Metal
Parts on Set
0.15 µF
Earth Ground
AC
Voltmeter
(0.75V)
Figure A. Using an AC voltmeter to check AC leakage.